Select a Machining Operation in the Manufacturing Program,
then select Tool Path Replay  . See
Replaying the Tool Path and Simulating Material Removal in Video Mode for general information. . See
Replaying the Tool Path and Simulating Material Removal in Video Mode for general information. In the Tool Path Replay dialog box, click Full
Video
 to simulate the material removal by the Machining Operation.
to simulate the material removal by the Machining Operation. The material removal video appears in a new window.

Start the comparison: - Click
Analyze
 . .
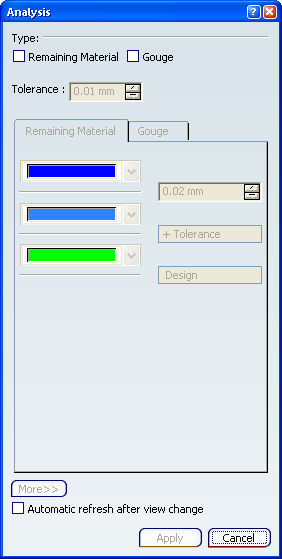
The Analysis dialog box appears.
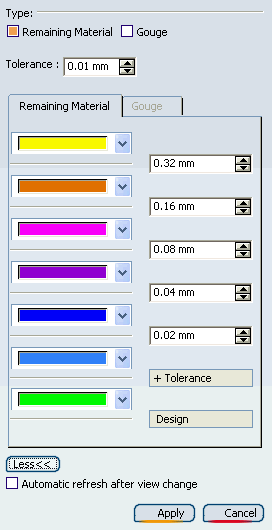
 By default,
the Remaining Material
tab displays three tolerance bands for analysis. More gives access to additional tolerance bands.
By default,
the Remaining Material
tab displays three tolerance bands for analysis. More gives access to additional tolerance bands.
- Select the Automatic refresh after view change
check box to refresh the window after a view change.
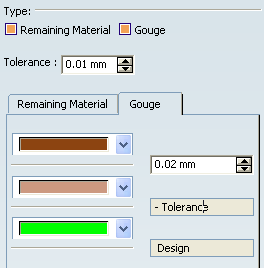
- Select the check box associated with the fault type
to be analyzed (Remaining Material or Gouge or both).
- Go to the corresponding tab and
specify the tolerance bands for the comparison.
The remaining material and gouges are displayed as colored
zones according to the specified tolerances.
- Click Apply.
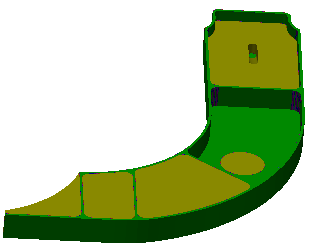
The machined part is compared with the design part, based on
the specified settings.
- Any point on the machined surface of the workpiece is considered
to be part of a fault if the distance (deviation) to the design
part surface is greater than the specified tolerance.
- The results of the comparison are reflected on the workpiece,
based on the extent of severity of the fault and the customized
color settings.
Still in video mode, pick a point on the machined stock.
The Pick Point Information dialog
box appears.
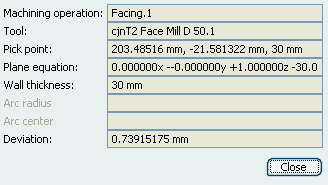
Notes:
- This information is available at every pick, provided that the point picked
is a "machined area pick".
- Arc radius and Arc center are populated only if the picked point is on
a circular entity.
- Deviation is displayed after you have compared the machined stock part and the target (design) part : the stock is rendered in
a color-coded manner, depicting deviations from the design part. A subsequent
pick displays the deviation value.
|