XML Mapping File | ||||||||||
|
| |||||||||
Mandatory Elements
The XML mapping file must be valid regarding the PropertyMappingRule.xsd schema that contains the description of the mapping file. Each time you update a mapping property, the whole XML file is parsed and the properties are applied to elements. Any difference between the xml file syntax and the .xsd description (spelling error, missing mandatory attribute...) generates an error message when you update the property.
To be valid, the XML mapping file requires the following elements:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ListOfProperties xmlns="urn:propertymappingrules" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="urn:propertymapping rules PropertyMappingRules.xsd"> <!-- file content --> </ListOfProperties>
The decimal point used in the exported XML mapping file depends on the regional settings of your operating system. It can be either a period or a comma (for example: 0.001 or 0,0001). No other symbol is supported; a warning message is displayed when you update the property if the decimal point used in the XML file does not correspond to the regional settings of your operating system. The name of the .xsd file also depends on the regional settings of your operating system:
- If the decimal point is a period, the .xsd file name must be PropertyMappingRules.xsd.
- If the decimal point is a comma, the .xsd file name must be PropertyMappingRules-fr.xsd.
![]()
Global Parameters
The XML mapping file contains global parameters (tolerance value, axis system, and units) that must be defined in the XML file.
Default Values
DEFAULT_VALUES is the keyword that specifies and defines the default tolerance and the default axis system.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| TOL | Default tolerance value that is used in the element identification to capture the element that is the closest to the specified coordinates in this given tolerance. | Mandatory |
| AXIS | Default axis system that is kept as the reference axis system for the element identification. By default, the axis system is the axis of the finite element model representation. This axis must be orthonormal. To define the axis system, you can use the axis coordinates or the name of the axis system (given in the specification tree). For example:
|
Mandatory |
| Important: Do not use the \ character in the name of the axis system. This character can only be used to define the path of the axis system. |
Units
UNITS is the keyword you that specifies the default units.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| LENGTH | Specifies the default length unit that is used in the XML file. | Mandatory |
| ANGLE | Specifies the default angle unit that is used in the XML file. | Mandatory |
Note: The syntax of the units is the same as specified in the unit settings .
![]()
Element Identification
The element identification lets you apply a property to finite elements. Two approaches are available: spatial or associative. When you generate an XML mapping file, the elements are identified using the spatial identification approach, but you can use both approaches in the same XML file.
Spatial Identification
The spatial identification is based on the coordinates (X, Y, Z) of the geometric center of finite elements. Use the spatial identification when more than one element is bounded by four geometries.
| Attributes | Description |
|---|---|
| X | Specifies the X-coordinate of a finite element. |
| Y | Specifies the Y-coordinate of a finite element. |
| Z | Specifies the Z-coordinate of a finite element. |
You can also specify an optional tolerance value to capture the element that is the closest to the specified coordinates in the given tolerance (TOL).
| Important: If you do not add an optional tolerance, the default tolerance that is defined in the XML Mapping File is taken into account in the element identification. |
Associative Identification
The associative identification is based on geometric reference path in the specification tree and allows you to capture elements that belong to a mesh, to a group, and to a geometry. You can also refine the element selection by identifying elements that share nodes with a mesh, a group, or a geometry.
| Attributes | Description |
|---|---|
| BELONG_TO_MP | Specifies all the finite elements that belong to a mesh. |
| BELONG_TO_GROUP | Specifies all the finite elements that belong to a group. |
| BELONG_TO_GEOM | Specifies all the finite elements that belong to a geometry. |
| SHARE_WITH_MP | Specifies all the finite elements that share at least one node with a mesh. |
| SHARE_WITH_GROUP | Specifies all the finite elements that share at least node with a group. |
| SHARE_WITH_GEOM | Specifies all the finite elements that share at least node with a geometry. |
Notes:
- You cannot use the SHARE_WITH criterion as the only associative identification. It is used to filter of the result of a BELONG_TO identification.
- You cannot use the BELONG_TO_GEOM keyword in the solid property definition.
- If no element is found, a warning message will be displayed when you update the property.
To identify geometries, use the specification tree path as follows: from the product where the finite element model representation is instanciated down to the geometry you want to identify, write the name of each feature and separate them using the \ character.
| Important: Do not use the \ character in the geometry names. |
To identify publications, use the specification tree path from the product where the finite element model representation is instanciated up to the product instance that contains the publication of the geometry as shown below:
Name of the product\Publications:Name of the published element
| Tip: Giving the complete specification tree path for geometries and publications is optional when the finite element model is linked to only one 3D shape, but mandatory when the finite element model is linked to several 3D shapes. |
Consider the following specification tree structure: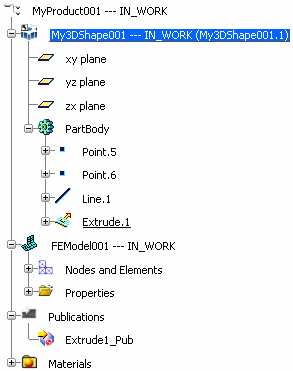
The Extrude.1 geometry is identified as follow:
BELONG_TO_GEOM="MyProduct001\My3DShape001\PartBody\Extrude.1"
The Extrude1_Pub publication is identified as follow:
BELONG_TO_GEOM="MyProduct001\Publications:Extrude1_Pub"
For finite elements on which you want to apply the same property with the same characteristics, you can use identification by intersection or identification by union, but you cannot mix the both identifications in the same keyword.
- Identification by Intersection
- You can use intersection of geometries or groups to identify finite
elements inside the same keyword by separating geometries, meshes, or groups using the ; symbol (no space around the
; symbol). The result of the selection is the
intersection of all the selected geometries, meshes, or groups.
You can also use the intersection by combining the BELONG_TO and SHARE_WITH keywords to refine your selection. This combination is possible if each keyword appears only once per XML line. The result of the selection is the intersection of each keyword results. For example:
- The following identification:
BELONG_TO_GEOM="Fill.1;Fill.2" SHARE_WITH_GROUP="Group.2"
means that you will first capture elements that belong to the intersection of Fill.1 and Fill.2 geometries and then filter the captured elements with elements that share at least one node with the Group.2 group. - Consider the Fill.1 geometry meshed with four frames (F1, F2, F3, F4) as constraints and the automatic capture mode:
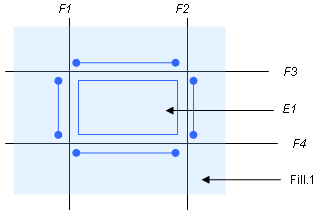
BELONG_TO_GEOM="Fill.1" SHARE_WITH_GEOM="F1;F2;F3;F4"
means that the defined property is applied to the elements that belong to the Fill.1 geometry and that share nodes with the frames F1, F2, F3, F4. E1 is the only element that satisfies those conditions.
- The following identification:
- Identification by Union
- You can use union of geometries, meshs or groups to identify
finite elements inside the same keyword by separating geometries, meshes, or groups using the + symbol (you can add a space
around the + symbol). The result of the selection is the
union of all the selected geometries, meshes, or groups.
Important: The union is possible only for the BELONG_TO_GEOM, BELONG_TO_MP and BELONG_TO keywords. The line:
<SHELL BELONG_TO_GEOM="Fill.1+Fill.2" TH="0.5" MAT="Material.1"/>
is equivalent to the two following lines:<SHELL BELONG_TO_GEOM="Fill.1" TH="0.5" MAT="Material.1"/> <SHELL BELONG_TO_GEOM="Fill.2" TH="0.5" MAT="Material.1"/>
Examples of Element Identification
X="0.0005" Y="-0.03" Z="0"
BELONG_TO_MP="Octree Triangle Mesh.1"
BELONG_TO_GROUP="Geometric Group.1"
SHARE_WITH_GEOM="PartBody\Fill.1"
![]()
Property Definition
You have to define the characteristics of the properties you want to apply to finite elements in the XML mapping file.
You can define in the XML mapping file the characteristics of the following properties:
- Beam Property
- Variable Beam Property
- Bar Property
- Shell Property
- Membrane Property
- Shear Panel Property
- Inhomogeneous Composite Shell Property
- Inhomogeneous Composite Membrane Property
- Inhomogeneous Composite Shear Panel Property
- Homogeneous Composite Shell Property
- Homogeneous Composite Membrane Property
- Homogeneous Composite Shear Panel Property
- Solid Property
Beam Property
BEAM is the keyword you have to use to apply a beam property.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | Specifies the material name. | Mandatory |
| MAT_DOMAIN | Specifies the material domain. If you do not specify a domain, the material domain set as default is automatically used. |
Optional |
| AREA | Specifies the area of the cross section. | Mandatory |
| INERTIA | Specifies the three components of the inertia matrix of the beam, expressed in the principal axis of the beam (Ixx, Iyy, Izz). | Mandatory |
| ORIENTATION_SURFACE or ORIENTATION_VECTOR or ORIENTATION_POINT | Specifies the orientation of the beam section using a vector or using a geometric point. See Beam Section Orientation. | Mandatory |
| SHEAR_CENTER | Specifies the y-coordinate and the z-coordinate of the shear center in the section axis, centered at the center of gravity of the section. If you do not specify this attribute, the default coordinates of the shear center is (0,0). | Mandatory |
| SHEAR_RATIO_XY | Specifies the ratio of the Y shear area over the cross-sectional area. If you do not specify this attribute, the default value is 0. | Mandatory |
| SHEAR_RATIO_XZ | Specifies the ratio of the Z shear area over the cross-sectional area. If you do not specify this attribute, the default value is 0. | Mandatory |
| OFFSET | Specifies the offset values at each end of the beam. The three first values are the components of the offset vector for the start node of the beam, and the last three values are the components of the offset vector for the end of the beam. This vector is defined in the local axis of the beam, and the offset direction is the finite element normal direction. If several elements are found during the associative identification, a linear interpolation is made to make the offset characteristic variable. You can also use the spatial identification of elements and define offset values for each element to make the offset characteristic variable. |
Optional |
| DOF_START | Specifies the released degrees of freedom of the start node of the element (0 to release a degree of freedom and 1 to fix a degree of freedom). If several elements are found during the associative identification, all the nodes between the start and the end nodes are fixed. |
Optional |
| DOF_END | Specifies the released degrees of freedom of the end node of the element (0 to release a degree of freedom and 1 to fix a degree of freedom). If several elements are found during the associative identification, all the nodes between the start and the end nodes are fixed. |
Optional |
Tip:
To find the start node and the end node and to visualize the implicit orientation of 1D elements imposed by the mesh, generate a Local axis image. The X-direction determines the start node, and the end node is determined as shown below: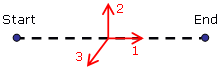 |
Variable Beam Property
BEAM_V is the keyword you have to use to apply a variable beam property.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | Specifies the material name. | Mandatory |
| MAT_DOMAIN | Specifies the material domain. If you do not specify a domain, the material domain set as default is automatically used. |
Optional |
| AREA | Specifies the area of the cross section. In the case of multi-selection of elements (associative identification), a linear interpolation of values is done between the start and end elements. |
Mandatory |
| INERTIA | Specifies the six components of the inertia matrix of the beam, expressed in the principal axis of the beam (Ixx1, Iyy1, Izz1, Ixx2, Iyy2, Izz2). In the case of multi-selection of elements (associative identification), a linear interpolation of values is done between the start and end elements. |
Mandatory |
| ORIENTATION_SURFACE or ORIENTATION_VECTOR or ORIENTATION_POINT | Specifies the orientation of the beam section using a surface, a vector, or a geometric point. See Beam Section Orientation. | Mandatory |
| SHEAR_CENTER | Specifies the y-coordinate and the z-coordinate of the shear center in the section axis, centered at the center of gravity of the section. If you do not specify this attribute, the default coordinates of the shear center is (0,0). | Mandatory |
| SHEAR_RATIO_XY | Specifies the ratio of the Y shear area over the cross-sectional area. If you do not specify this attribute, the default value is (0;0). In the case of multi-selection of elements (associative identification), a linear interpolation of values is done between the start and end elements. |
Mandatory |
| SHEAR_RATIO_XZ | Specifies the ratio of the Z shear area over the cross-sectional area. If you do not specify this attribute, the default value is (0;0). In the case of multi-selection of elements (associative identification), a linear interpolation of values is done between the start and end elements. |
Mandatory |
| OFFSET | Specifies the offset values at each end of the beam. The three first values are the components of the offset vector for the start node of the beam, and the last three values are the components of the offset vector for the end of the beam. This vector is defined in the local axis of the beam, and the offset direction is the finite element normal direction. If several elements are found during the associative identification, a linear interpolation is made to make the offset characteristic variable. You can also use the spatial identification of elements and define offset values for each element to make the offset characteristic variable. |
Optional |
| DOF_START | Specifies the released degrees of freedom of the start node of the element (0 to release a degree of freedom and 1 to fix a degree of freedom). If several elements are found during the associative identification, all the nodes between the start and the end nodes are fixed. |
Optional |
| DOF_END | Specifies the released degrees of freedom of the end node of the element (0 to release a degree of freedom and 1 to fix a degree of freedom). If several elements are found during the associative identification, all the nodes between the start and the end nodes are fixed. |
Optional |
Tip:
To find the start node and the end node and to visualize the implicit orientation of 1D elements imposed by the mesh, generate a Local axis image. The X-direction determines the start node, and the end node is determined as shown below: |
Bar Property
BAR is the keyword you have to use to apply a bar property.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | Specifies the material name. | Mandatory |
| MAT_DOMAIN | Specifies the material domain. If you do not specify a domain, the material domain set as default is automatically used. |
Optional |
| AREA | Specifies the area of the cross section. | Mandatory |
Shell Property
SHELL is the keyword you have to use to apply a shell property.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | Specifies the material name. | Mandatory |
| MAT_DOMAIN | Specifies the material domain. If you do not specify a domain, the material domain set as default is automatically used. |
Optional |
| TH | Specifies the thickness value. The thickness value must be greater than zero. | Mandatory |
Membrane Property
MEMBRANE is the keyword you have to use to apply a membrane property.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | Specifies the material name. | Mandatory |
| MAT_DOMAIN | Specifies the material domain. If you do not specify a domain, the material domain set as default is automatically used. |
Optional |
| TH | Specifies the thickness value. The thickness value must be greater than zero. | Mandatory |
Shear Panel Property
SHEAR_PANEL is the keyword you have to use to apply a shear panel property.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | Specifies the material name. | Mandatory |
| MAT_DOMAIN | Specifies the material domain. If you do not specify a domain, the material domain set as default is automatically used. |
Optional |
| TH | Specifies the thickness value. The thickness value must be greater than zero. | Mandatory |
Inhomogeneous Composite Shell Property
COMPOSITE_SHELL is the keyword you have to use to apply a composite shell property with a ply approach.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| LAMINA | Defines the lamina. See the Lamina Definition. | Mandatory |
| REF_ANGLE | Specifies an offset in the angle definition for each element. You can then vary all the angles by entering only one value in the local axis of the finite element. | Optional |
| COMPOSITE_AXIS | Specifies an axis system. If this attribute is not specified, the default axis system is the one defined in the global parameters at the beginning of the XML file. | Optional |
| Important: REF_ANGLE and COMPOSITE_AXIS are not compatible. If the both attributes are defined in the same line, COMPOSITE_AXIS will be ignored when you import the XML mapping file. |
Inhomogeneous Composite Membrane Property
COMPOSITE_MEMBRANE is the keyword you have to use to apply a composite membrane property with a ply approach.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| LAMINA | Defines the lamina. See the Lamina Definition. | Mandatory |
| REF_ANGLE | Specifies an offset in the angle definition for each element. You can then vary all the angles by entering only one value in the local axis of the finite element. | Optional |
| COMPOSITE_AXIS | Specifies an axis system. If this attribute is not specified, the default axis system is the one defined in the global parameters at the beginning of the XML file. | Optional |
| Important: REF_ANGLE and COMPOSITE_AXIS are not compatible. If the both attributes are defined in the same line, COMPOSITE_AXIS will be ignored when you import the XML mapping file. |
Inhomogeneous Composite Shear Panel Property
COMPOSITE_SHEAR_PANEL is the keyword you have to use to apply a composite shear panel property with a ply approach.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| LAMINA | Defines the lamina. See the Lamina Definition. | Mandatory |
| REF_ANGLE | Specifies an offset in the angle definition for each element. You can then vary all the angles by entering only one value in the local axis of the finite element. | Optional |
| COMPOSITE_AXIS | Specifies an axis system. If this attribute is not specified, the default axis system is the one defined in the global parameters at the beginning of the XML file. | Optional |
| Important: REF_ANGLE and COMPOSITE_AXIS are not compatible. If the both attributes are defined in the same line, COMPOSITE_AXIS will be ignored when you import the XML mapping file. |
Homogeneous Composite Shell Property
COMPOSITE_SHELL_H is the keyword you have to use to apply a composite shell property with a zone approach.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| LAMINA | Defines the lamina. See the Lamina Definition. | Mandatory |
| REF_ANGLE | Specifies an offset in the angle definition for each element. You can then vary all the angles by entering only one value in the local axis of the finite element. | Optional |
| COMPOSITE_AXIS | Specifies an axis system. If this attribute is not specified, the default axis system is the one defined in the global parameters at the beginning of the XML file. | Optional |
| Important: REF_ANGLE and COMPOSITE_AXIS are not compatible. If the both attributes are defined in the same line, COMPOSITE_AXIS will be ignored when you import the XML mapping file. |
Homogeneous Composite Membrane Property
COMPOSITE_MEMBRANE_H is the keyword you have to use to apply a composite membrane property with a zone approach.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| LAMINA | Defines the lamina. See the Lamina Definition. | Mandatory |
| REF_ANGLE | Specifies an offset in the angle definition for each element. You can then vary all the angles by entering only one value in the local axis of the finite element. | Optional |
| COMPOSITE_AXIS | Specifies an axis system. If this attribute is not specified, the default axis system is the one defined in the global parameters at the beginning of the XML file. | Optional |
| Important: REF_ANGLE and COMPOSITE_AXIS are not compatible. If the both attributes are defined in the same line, COMPOSITE_AXIS will be ignored when you import the XML mapping file. |
Homogeneous Composite Shear Panel Property
COMPOSITE_SHEAR_PANEL_H is the keyword you have to use to apply a composite shear panel property with a zone approach.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| LAMINA | Defines the lamina. See the Lamina Definition. | Mandatory |
| REF_ANGLE | Specifies an offset in the angle definition for each element. You can then vary all the angles by entering only one value in the local axis of the finite element. | Optional |
| COMPOSITE_AXIS | Specifies an axis system. If this attribute is not specified, the default axis system is the one defined in the global parameters at the beginning of the XML file. | Optional |
| Important: REF_ANGLE and COMPOSITE_AXIS are not compatible. If the both attributes are defined in the same line, COMPOSITE_AXIS will be ignored when you import the XML mapping file. |
Lamina Definition
LAMINA is the keyword you have to use to define lamina in composite properties.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | Specifies the material name. | Mandatory |
| MAT_DOMAIN | Specifies the material domain. If you do not specify a domain, the material domain set as default is automatically used. |
Optional |
| ANGLE | Specifies the angle of each lamina. | Mandatory |
| TH | Specifies the thickness of each lamina. This attribute is optional if the Cured thickness value has been already set in the properties of a composite material behavior. | Optional |
| POSITION | Defines several layers with the same characteristics but with a specific order. | Mandatory for inhomogeneous composite properties |
| MULTIPLICATION_FACTOR | Defines several layers with the same characteristics. This attribute is optional if the associated value is equal to 1. | Mandatory for homogeneous composite properties |
Solid Property
SOLID is the keyword you have to use to apply a solid property.
| Attributes | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | Specifies the material name. | Mandatory |
| MAT_DOMAIN | Specifies the material domain. If you do not specify a domain, the material domain set as default is automatically used. |
Optional |
| AXIS | Specifies an axis system to orient the orthotropic material. The X, Y, and Z coordinates are not transformed by this axis system. Those coordinates are interpreted in the global axis system in the XML file. | Optional |
| AXIS_TYPE | Specifies the type of the axis system: CARTESIAN, CYLINDRICAL or SPHERICAL. | Optional |
Examples of Property Definition
Examples of a beam property:
<BEAM X="-0.01" Y="0.035" Z="0" AREA="0.05" INERTIA="1;1;1" ORIENTATION_POINT="0;1;0" MAT="Material.1" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic01"/>
<BEAM X="36.01" Y="9.99" Z="19.99" AREA="0.0003" INERTIA="2e-8;1e-8;1e-8" SHEAR_RATIO_XY="1.2" SHEAR_RATIO_XZ="1.2" SHEAR_CENTER="0;0" ORIENTATION_VECTOR="1;0;0" MAT="Material.1" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic02"/>
Example of a bar property that is using the default material domain:
<BAR X="-39.993" Y="-2.716" Z="5.793" MAT="Material.1" MAT_DOMAIN="" AREA="0.03"/>
Example of a 2D shell property:
<SHELL X="-32.95" Y="0.38" Z="0" TH="0.001" MAT="Material.1" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic01"/>
Example of a 2D membrane property:
<MEMBRANE X="3.4035" Y="9.9999" Z="19.9652" TH="0.002 MAT="Material.1" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic01"/>
Example of a 2D shear panel property:
<SHEAR_PANEL X="5.80" Y="-18.05" Z="1.26e-07" TH="0.001" MAT="Material.1 MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic01""/>
Example of a composite membrane property with the zone approach:
<COMPOSITE_MEMBRANE_H X="0.035" Y="-0.03" Z="0"
COMPOSITE_AXIS="Axis Systems\Axis System.2">
<LAMINA MAT="Material002" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic02" TH="0.004" ANGLE="60"/>
<LAMINA MAT="Material002" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic02" TH="0.008" ANGLE="90"/>
<LAMINA MAT="Material002" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic02" TH="0.001" ANGLE="120"/>
</COMPOSITE_MEMBRANE_H>Example of a composite shear panel property with the zone approach and a multiplication factor:
<COMPOSITE_SHEAR_PANEL_H X="0.005" Y="0.035" Z="0"
COMPOSITE_AXIS="Axis Systems\Axis System.2">
<LAMINA MAT="Material002" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic02" TH="0.001" ANGLE="30"
MULTIPLICATION_FACTOR="4"/>
</COMPOSITE_MEMBRANE_H>Example of a 3D property:
<SOLID X="-37.959" Y="-9.294" Z="1.983" BELONG_TO_MP="Surface Mesh.2" MAT="Material001" MAT_DOMAIN="LinearElastic01"/>