About the View Generation Modes | ||||
|
| |||
Configuration of View Generation Modes
You can configure the view generation modes through Tools > Options... > Mechanical > Drafting > Generation tab.
In this case, it will be used when creating new views. Refer to View for more information.
Once the view has been created, you can modify its properties through the Properties dialog box: from the contextual menu of a given view, select Properties, click the Generation tab and then select the desired options. For more information, refer to Generation Tab.
| Important: In the case of CGR, Approximate and Raster views, generated geometry is not associative and cannot be detected. For these views, only interactive geometry and axes can be detected. |
![]()
Exact view
Exact views are generated from the Design mode: they are views for which the geometry is available. The exact generation mode will be the best option in most cases:
- This is the fastest generation mode.
- All types of views can be generated using this option.
- Each functionality (dress-up, dimensions, annotations, etc.) is available.
Note: The edges of faces with a relative angle of less than 0.5 degrees are considered as being "smooth edges", and therefore are not represented.
However, there are a few cases in which choosing the exact generation mode will not be appropriate:
- In the case of sophisticated products or assemblies involving large amounts of data, generating exact views may consume too much memory.
- The edges of faces with a relative angle of less than 0.5 degrees are considered as being "smooth edges", and therefore are not represented.
- Polyhedral elements (such as surfaces, wireframes, etc.) from V4 .model documents are not supported.
| Important:
Clashes correspond to collisions between two parts in an assembly or two bodies in a part. Clashing bodies may be incorrectly projected in exact projection and section views: some edges of these bodies may appear whereas they should be hidden, or may disappear whereas they should not be hidden. The missing edges are normally seen as hidden edges, and can be visualized when activating Hidden Lines for the view. The image below shows clashing bodies in a 3D representation: 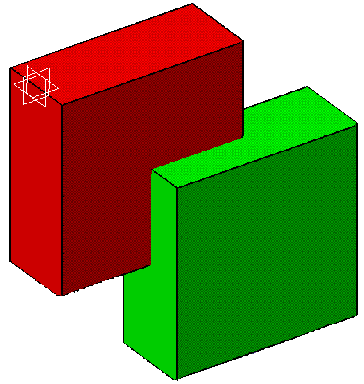 The image below shows clashing bodies incorrectly projected in an exact view: 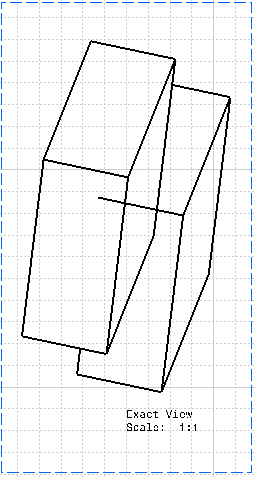 The image below shows clashing bodies correctly projected in an approximate view: 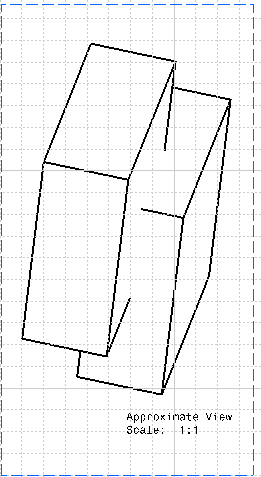 The image below shows clashing bodies correctly projected in a raster view: 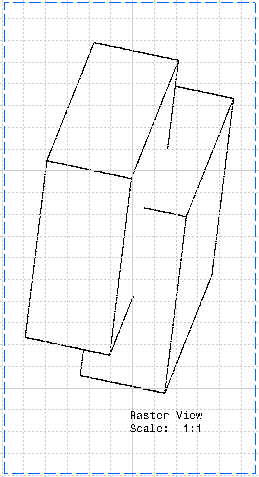 The image below shows clashing bodies correctly projected in a CGR view: 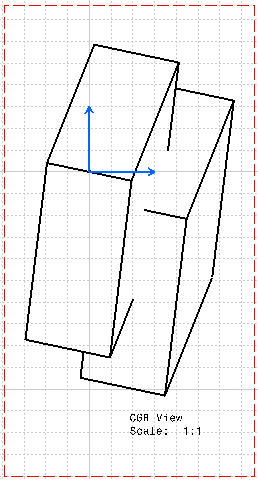 To avoid such clashes and ensure that the edge representing the border of the collision will be projected, you can modify the assembly or part using either of the following methods:
To ensure that a screw in a threaded hole is not considered as a clash in a section view or a breakout view, you must design the screw as a whole 3D part representation, apply a thread feature to the screw, and create the hole as a threaded hole (refer to Part Design User's Guide: Creating threaded holes). Then, on the part instance associated to the screw, you must either:
|
![]()
Approximate view
Approximate views are generated using the Approximate mode. Although Approximate views are not as high in precision and quality as exact views, this generation mode dramatically reduces memory consumption. Performances may also be improved, depending on how you fine-tune precision. Therefore, the Approximate mode is particularly well-adapted to sophisticated products or assemblies involving large amounts of data.
The Approximate mode offers about the same advantages and restrictions than the CGR generation mode (refer to About the View Generation Modes). However, there are some differences:
- Approximate consumes even less memory than CGR.
- Approximate is faster than CGR, but performances largely depend on fine-tuning.
- Approximate provides more approximate results than CGR, but these results largely depend on how you fine-tune precision.
- Approximate lets you generate section views, section cuts and breakout views. However, note that certain restrictions apply, which are documented in other parts of this user's guide, when appropriate.
For more information about the advantages and restrictions associated with the Approximate generation mode, see About the View Generation Modes below.
![]()
Raster view
Raster views are generated as images. This enables you to quickly generate overall views for large products or assemblies, regardless of drawing quality. Such views are associative to the 3D geometry and can be updated when the part or product changes.
Restrictions
Raster views involve a number of restrictions:
- You cannot generate the following types of views using this option: view from 3D, section views, section cuts, detail views, breakout views, unfolded views.
- Raster views cannot contain dress-up elements (axis, center lines, threads).
- Creating dimensions is impossible.
- Generally speaking, all commands requiring the selection of geometry are not available.
- Raster views cannot be edited (you can work around this by isolating the view: double-clicking the image will then launch an image editor).
As a consequence of these restrictions, selecting this option disables a number of other options on the View and on the Generation tab (available through Tools > Options... > Mechanical > Drafting) or in the Properties dialog box (available through Edit > Properties).
Overloading colors/graphic properties
When the color of a product instance is overloaded at the product level, this color is applied in the raster view to the elements contained in this product (including edges, faces, points and lines).
When other graphic properties are overloaded at the product level, they are lost in the raster view (contrary to an exact view).
![]()
CGR view
CGR views are generated using the CGR format (CATIA Graphical Representation) of the 3D geometry. A CGR format only contains a graphical representation of the geometry, which is available with the Visualization mode (as opposed to the exact geometry, which is available with the Design mode). The CGR view uses and displays only the external appearance of the component; the geometry is not available. The corresponding .cgr file, if it exists, is inserted from the cache system.
To generate a correct CGR view from an assembly composed of .cgr files, use only high quality .cgr files, containing data about edges and faces. For example, a .cgr file created with DMU Optimizer miss this information (to be as light as possible). In this particular case, the CGR view mode can produce unpredictable results.
CGR views are not as high in quality as exact views, but they consume much less memory during the generation. This may be useful when dealing with sophisticated products or assemblies involving large amounts of data. However, this generation mode is rather slow.
For more information about the advantages and restrictions associated with the CGR generation mode, see About the View Generation Modes below.
![]()
Advantages and restrictions common to CGR and Approximate
Using CGR or Approximate to generate views offers the following advantages:
- Optimize memory consumption when generating and handling projection views for large products or assemblies.
- Generate views from third-party data (such as MultiCAD), as well as from polyhedral elements (such as dittos, surfaces, etc.) in V4 .model documents. Be careful to use only high quality .cgr files, containing data about edges and faces. For example, a .cgr file created with DMU Optimizer miss this information (to be as light as possible). In this particular case, the CGR and Approximate view modes can produce unpredictable results.
However, the CGR or Approximate generation mode involves a number of restrictions:
- You cannot generate the following types of views:
- For CGR: section views, section cuts, detail views, detail view profile, breakout views, unfolded views and views from 3D.
- For Approximate: detail views, detail view profile, unfolded views and views from 3D.
- The following types of elements are not associative on CGR or Approximate
views:
- For CGR: Auxiliary view profiles, annotations, dimensions, etc.
- For Approximate: Auxiliary view profiles, annotations, etc. Dimensions may now be associative, depending on whether you select the Allow the creation of associative dimension in approximate views option in the Dimensions associativity on 3D dialog box (see Dimension settings).
- You cannot project 3D elements such as wireframe, points, etc. on CGR or Approximate views.
- CGR or Approximate views cannot contain dress-up elements (axis, center lines, threads).
- Persistency of graphical properties edition (color, line type, line thickness, no show) and Delete operations performed on generated elements are not available on CGR or Approximate views.
- CGR or Approximate views being only a graphical representation of the geometry, only line segments are generated in such views. In the case of non-associative dimensions (as is always the case for CGR views, and may be the case for Approximate views when the Allow the creation of associative dimension in approximate views option is not selected), the only elements that can be dimensioned are these line segments. As a result, you may not be able create certain types of radius or diameter dimensions in such views.
- CGR or the Approximate option disables a number of other options on the View and on the Generation tab (available through Tools > Options... > Mechanical > Drafting) or in the Properties dialog box (available through Edit > Properties).
- Approximated items cannot be multi-selected using the mouse (trap selection).
However you can click
 to
select and edit the properties of a single item. Note that you can also multi-select
several items using the
Ctrl
key.
to
select and edit the properties of a single item. Note that you can also multi-select
several items using the
Ctrl
key.
- Approximated items cannot be duplicated. The Duplicate command is not available using contextual menu on an approximated item.
- The mesh thickness has an impact on the CGR and approximate view performance. Moreover, a CGR view cannot be computed from an extremely thin mesh, i.e. when the mesh on a single face consists of more than 6500 triangles. In this special case, you must raise the 3D accuracy (using Tools > Options > General > Display > Performance tab > 3D Accuracy options) before projecting a CGR view.
As a consequence of these restrictions, selecting either the CGR or the Approximate option disables a number of other options on the View and on the Generation tab (available through Tools > Options... > Mechanical > Drafting) or in the Properties dialog box (available through Edit > Properties).