Modifying 2D Texture Properties | |||||||
|
| ||||||
Double-click a material domain in the specification tree.
Click the Rendering tab in the Domain Edition dialog box:
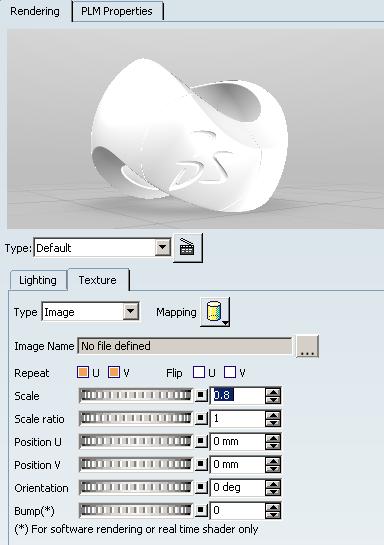
In the Type box, select the type of texture you want to apply.
In the Image Name box, navigate to locate the desired image, and click OK to map it onto the preview element as the texture.
For more information about image formats refer to About Image Formats
Click Change Mapping type
 to choose from the different mapping types :
to choose from the different mapping types :
Planar Spherical Cylindrical Cubical Auto Adaptive Manual Adaptive The Automatic Adaptive Mapping automatically creates a planar mapping on each object face.
During the automatic adaptive mapping operation, the surface may show a discontinuity in texture, as displayed below:
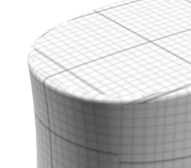
Automatic Adaptive MappingIt can be made continuous by manual mapping, provided the curvature of the surface is not too high, as shown below:
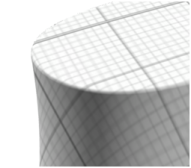
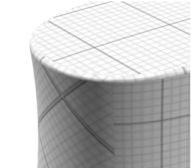
Manual Adaptive Mapping (Mini) Manual Adaptive Mapping (Maxi)Manual Adaptive Mapping gathers together faces which have close normal vectors. For each group of faces, a unique planar mapping is applied. The precision value defined using the slider modifies the tolerance used during the grouping process: the lower the precision, the more faces with greatly different normal vectors are gathered together. This manual mapping enables textures to cross slightly sharpen edges, thus providing a higher visual quality.
For more information on the mapping types refer to About 3D Textures in the Realistic Rendering User's Guide.
If necessary, change the Material size to adjust the scale of the material relative to the part.
Define the image scale, its position and its orientation:
U and V correspond to parameters of the local parametric surface.
- Repeat U, V
- Flip U V
- Scale ratio
- Position U, V
- Orientation
Use the Flip U and Flip V check boxes to invert the material texture along U and V axes.
You can click Links U and V scales
 to resize U and V proportionally. This is especially useful for square
shapes like floor material for instance. When this option is on, the
Scale V box is grayed and the icon changes to
to resize U and V proportionally. This is especially useful for square
shapes like floor material for instance. When this option is on, the
Scale V box is grayed and the icon changes to
 .
.The Bump slider lets you create a bump mapping effect when applying 2D textures. For more information on the bump mapping refer to the Bump Mapping Effect in the More about Modifying Material Texture Properties section.
Click OK to validate the material texture definition. The material icon reflects the material as defined. Note that there is no specific order for defining parameters.
Position the material interactively using the robot as explained in Materials.