About Harness Coverings | |||||||
|
| ||||||
Protective Covering Properties
Protective covering properties can be browsed in the Electrical tab of the Properties dialog box.
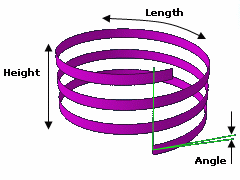
Total Tape Length
The total tape length is the tape length necessary to cover the segments. This value depends on the taping angle, the covered length and the number of layers.
Total tape length =
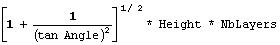
where:
- Angle is the angle at which the tape is wrapped round the segment.
- Height is the segment length covered by the tape.
- NbLayers is the number of layers of tape.
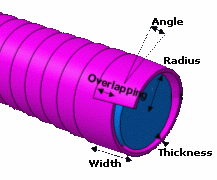
The overlap is the width of tape shared by two consecutive rolls around the segment. Overlap is computed as follows.
Overlap = Width - 2 PI *(Radius + Thickness/2) * Sin (Angle)
Where:
- Width is the width of the tape.
- Radius is the segment radius.
- Thickness is the thickness of the tape.
- Angle is the taping angle.
Notes:
- The taping angle and overlap are mutually exclusive parameters: enter the value of one of these parameters and the other is computed automatically.
- You can enter a negative overlap.
![]()
Relationships between Harness Components
You can change the relationships between the harness components.
By default, retainers are always placed on top, and protective tape is always placed over a segment. The diameter or shape of these components automatically adapts itself to the diameter of the components they cover. However, there may be times when you want to change the relationships between components or even, correct a component that is not properly positioned, in order to better represent the various layers of protective coverings and supports on top of segments.
The Adjust command lets you change the relationship between protective tape, retainers, and the components they cover: segments and protective coverings. For example, you can re-position protective tape placed on top of a segment and have it placed over another protective covering added to the same segment at a later date. Note that the graphical representation of the protective tape, retainer reflects the relationships defined between components. This gives you a better representation of components as well as accurate information letting you plan for manufacturing. Knowing which component is on top of which other component means you can deduce the placement order of protective coverings and supports during the process planning stage.
Notes:
- You cannot place a single protective covering over several segments.
- Supports can be added to segments already covered by a protective covering.
- You cannot place supports over other supports.
- Standard supports and corrugated tube come in fixed diameters and are positioned with respect to the segment routed inside them. By default, they are the outermost components. However, you can place protective tape over these components using the Adjust command.
- Protective coverings have a uniform circular shape over the entire
length of the covering. This means that:
- The shape of protective coverings does not change to match the
shape of other protective coverings or supports that are placed
over it:
- Protective tape may clash with supports:
- The inner diameter of corrugated tube does not change to match
the different diameters of a segment. The diameter remains constant.
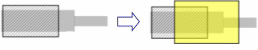
- The shape of protective coverings does not change to match the
shape of other protective coverings or supports that are placed
over it:
- Protective coverings and multi-profile branches: Protective coverings
do not handle multiple profiles: they keep circular profiles only.
The radius of the profile for protective tape is computed as follows:
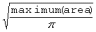
Protective Coverings for Flat Cables
A protective covering adapts itself to the segment, but not to flat cables because of their rectangular profile type.
| Warning: You can insert protective covering only on circular segments. |
If you create a circular protective covering auround a flat cable, the Width of the flat cable will be taken into account:
internal diameter of the protective covering = Width of the flat cable
For more information about adaptive diameter, please refer to the Electrical Library User's Guide: Creating Protective Coverings.