About LCM language | ||
| ||
Architecture
A LCM program is structured with modules. The module hierarchy is a tree.
See below an example of a Simulation Logic.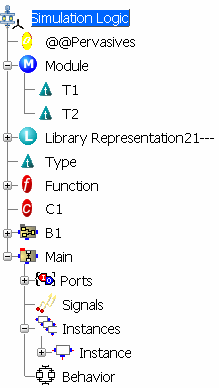
The elements of a LCM program are:
| Icon | Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|
 |
Simulation Logic | Root module of the LCM program. |
 |
Module | Modules are structured units to package together related components. See Defining Modules. |
 |
Library | Libraries of LCM elements. See Using Existing Libraries |
 |
Type | User-defined types. See Defining Types |
 |
Constant | User-defined constants. See Defining Constants |
 |
Function | User-defined functions See Defining Functions |
 |
Block | Blocks are execution units. See Defining Blocks |
 |
Pervasives | Standard library containing the pre-defined logic components: types, functions, constants and blocks. See Predefined Types and Functions |
Scoping
The visibility is bottom up. That is to say that a LCM element such as a type, a constant, a function or a block can only see (and so access) an element above it in the Simulation Logic tree.
This rule is also applied inside modules. For instance, in the specification tree, you can use the type T2 to define the type T1 but you cannot use T1 to define T2.
To re-order LCM elements in the specification tree, you can use the drag and drop command.
![]()
Verification at Edition
When the Simulation Logic is built, the following checks are done:
- Syntax: Validity of the expression syntax.
- Scope: Check if the elements used (constants, types, and so on) are defined or if they are visible from the current element.
- Typing: Check if the types of the mapped elements or the elements of an expressions are compatible.
Elements in error are highlighted in red in the specification tree.
Some other checks defined in the options can be enabled (see section Customizing > General). The elements raising a warning are identified in light red in the specification tree.