Click New Function
 and select an element of the Logic tree. .
and select an element of the Logic tree. .
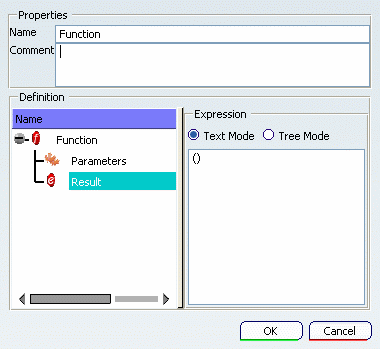
The Function Properties dialog box is displayed
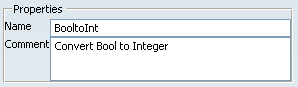
Change the name of the function. Add a comment if necessary.
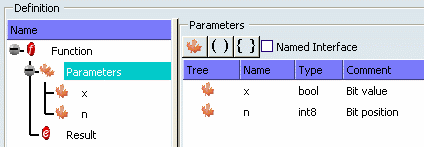
Set the input parameters:
- Click twice on Add Param
- Set the parameters names x and
n.
- Select the type of the parameters using the combo.
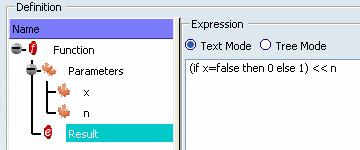
Set the result expression as shown
below.
The expression result is built from functions and constants visible in the scope of the current function. That is to say functions and constants :
- defined in the pervasives library ( see Predefined Types and Functions)
- or defined by the user and set above the current function in the specification tree.
Click OK.
The function is added to the tree (see a typical
example below ).
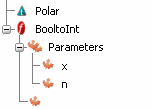
Click New Function and define the function PolartoCartesian as follows:
and define the function PolartoCartesian as follows:
- Add an input parameter and check Named Interface. The type Polar is a user defined type defined in the task Defining Types.
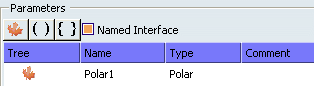
- Select Result in the left frame.
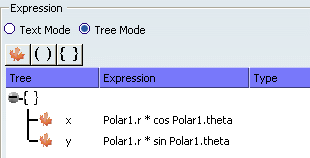
- Check Tree Mode and create a structure of two elements as follows:
Note:
Tree Mode is more convenient if the output has a structured data type. If you check Text Mode, you have to fill the complete syntax of the structured expression {x = Polar1.r * cos Polar1.theta; y = Polar1.r * sin Polar1.theta}.
Click OK.
The function is added to the specification tree.
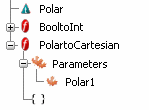
Now, you can insert the call of a function in a block. See Function Call in the SFC+ Editor and Function Call in the Block Editor.