You can define a structured data type using structures and tuples.
Click New Type
 and select the logic root.
and select the logic root.
The Type Properties dialog box appears:
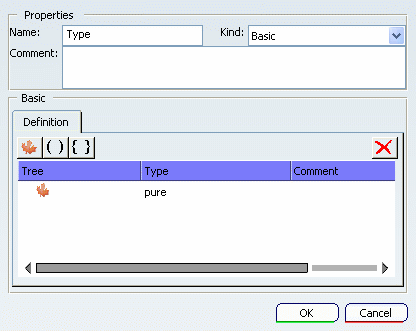
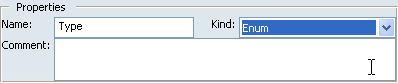
Change the type name. If needed, add a comment.
Click Add Element
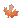 . This action creates a
structure with a child having a default name. The name can be changed
by clicking it and editing the field.
. This action creates a
structure with a child having a default name. The name can be changed
by clicking it and editing the field.
Repeat the previous step to add a second element to the structure.
Change the default names as defined below:
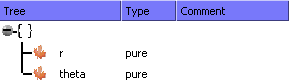
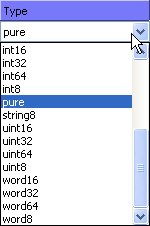
To change the type of the structure elements, drop-down
the combo-box. Select float64 in the type list:

If needed, add a comment to the elements structure.

Click OK.
The Polar type appears
in the tree.
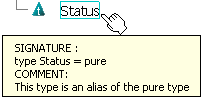
Scroll over Polar in the specification tree
to see its signature.

Note:
In a structure declaration, elements are separated by a ";" and labels are followed by ":" .
Double-click Polar in the specification tree to re-edit it.
Right-click the root and select Redefine as > Tuple. This command converts the existing structure into tuple.
Click OK.
Scroll over Polar in the specification tree
to see its signature.

Note:
In a tuple declaration, elements are separated by a
"*".
![]()



 . This action creates a
structure with a child having a default name. The name can be changed
by clicking it and editing the field.
. This action creates a
structure with a child having a default name. The name can be changed
by clicking it and editing the field.





 to add a member at the enumeration list.
to add a member at the enumeration list.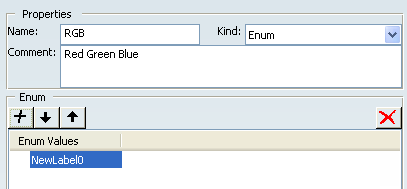
 and/or
and/or
 to sort the elements.
to sort the elements.