More about Variable Radius Fillets | ||||
|
| |||
Variable Radius Fillet Dialog Box
In this dialog box, you can define a variable radius fillet using these options:
- Edit Fillet Values
You can click Edit Fillet Values
 at the right of the Radius box to display the Fillet values dialog box.
at the right of the Radius box to display the Fillet values dialog box. 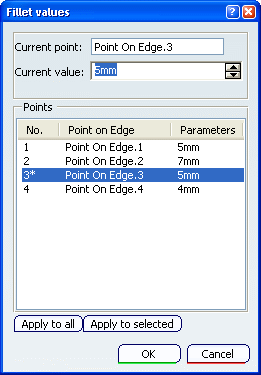
The Points area lists all the points of the part used to form the variable radius fillets and the radius values applied at these points. If you select any of these values, the corresponding constraint is highlighted in the geometric area (and vice-versa).
You can click Apply to all to set all the parameters to the value (or the parameter definition) chosen in the Current value box.
You can click Apply to selected to set the selected parameters to the value (or the parameter definition) chosen in the Current value box.
Tip: To sort the list by name and value, click on Point on Edge and Parameters tab respectively. - Selection Mode
- Two selection modes are available:
- Minimal: edges tangent to selected edges can be taken into account to some extent. The application continues filleting beyond the selected edge whenever it cannot do otherwise.
- Tangency: tangencies are taken into account so as to fillet entire edges. If you set the Tangency mode, the Trim ribbons option becomes available: you can then trim the fillets to be created. For more information, see Creating Edge Fillets. The tangent continuous edges of the selected edge are managed to ensure a better fillet stability and robustness (more fillets are automatically rerouted in case of design changes).
- Variation
- This is the fillet you would obtain using the Linear
variation mode. Examine the difference:
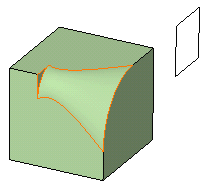
- Conic Parameter
The Conic Parameter option allows you to vary the section of the fillet. For a parameter comprised between or equal to:
-
0.5, the resulting curve is a parabola.
-
0 < parameter < 0.5, the resulting curve is an arc of an ellipse.
-
0.5 < parameter < 1, the resulting curve is a hyperbola.
If the conic mode is activated, the Edge(s) to keep and the No internal sharp edge options cannot be selected.
Conical fillets do not handle twist configurations. If a twist is detected, the fillet operation fails.
If the fillet surface curvature is lower than the support curvature, fillet surface relimitation may fail. In such cases, you need to decrease the conic parameter.
-
- Points
- Contextual commands for creating the points you need are available
in the Points box.
- Insert Wireframe > Create Point: For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Creating Wireframe Geometry: Creating Points.
- Insert Wireframe > Create Midpoint: Creates the midpoint of the line you select.
- Insert Wireframe > Create Endpoint: Creates the endpoint of the line you select.
- Insert Wireframe > Create Intersection: For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Creating Wireframe Geometry: Creating Intersections.
- Insert Wireframe > Create Projection: For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Creating Wireframe Geometry: Creating Projections.
- Insert Wireframe > Create Plane: For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Creating Wireframe Geometry: Creating Planes. If you create any of these elements, the application then displays the corresponding icon close to the Points box. Clicking this icon enables you to edit the element.
- To add additional points on the edge to be filleted, you can
also select planes. The application computes the intersections
between these planes and the edge to determine the useful
points.
In this example, three planes are selected. Now, if you move these
planes later, the application will compute the intersections again
and modify the fillet accordingly.
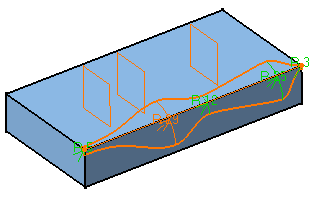
- Points can be added too by selecting 3D points.
- Contextual commands for creating the points you need are available
in the Points box.
- No Internal Sharp Edge
When computing variable radius fillets, the application may generate unexpected sharp edges when the surfaces to be connected are continuous in tangency but not continuous in curvature. In order to improve your design, just select the No internal sharp edges check box. This removes all possibly generated edges.
Note that this option does not work with the Keep edge option, whatever mode you are working with (explicit or implicit mode). For more information, see Creating Edge Fillets.
- Edges to Keep
This option specifies the edges which you do not want to fillet while running the fillet operation on the edges of interest. For more information about Edge(s) to keep, see Creating Edge Fillets.
Important: - This option is available only if you are defining a constant edge fillet using Variable Radius Fillet
 (that is a fillet which different radius values are equal).
(that is a fillet which different radius values are equal). - You can use Edge(s) to keep option to create variable radius fillet with only Cast and Forged Part Optimizer license.
- This option is available only if you are defining a constant edge fillet using Variable Radius Fillet
- Blend Corners
For more information on Blend corners option, see Reshaping Corners.
- Variable Radius Fillet Using a Spine
Sometimes, you will need to fillet consecutive edges with no tangent continuity that you would like to treat logically as a single edge. You can do this by using a spine. Compare the fillets below:
- Standard Fillet
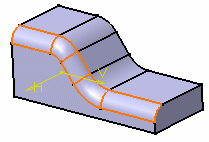
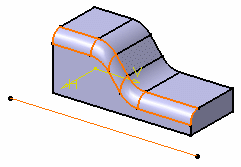
- Fillet Using a Spine
To fillet the edge, the application uses circles contained in planes normal to the spine. It is then possible to control the shape of the fillet.
The spine can be a wireframe or a sketcher element.
The Generative Shape Design product license is required to access this capability.

- Limiting Elements
- It is possible to use one or more limiting elements.
-
Contextual commands
creating the limiting elements you need are available from the
Limiting elements box:
- Create Point: For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Creating Wireframe Geometry: Creating Points.
- Create Midpoint: Creates the midpoint of the line you select.
- Create Endpoint: Creates the endpoint of the line you select.
- Create Plane: For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Creating Wireframe Geometry: Creating Planes.
- XY Plane: The XY plane of the current coordinate system origin (0,0,0) becomes the limiting element.
- YZ Plane: The YZ plane of the current coordinate system origin (0,0,0) becomes the limiting element.
- ZX Plane: The ZX plane of the current coordinate system origin (0,0,0) becomes the limiting element.
- Create Intersection: For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Creating Wireframe Geometry: Creating Intersections.
- Create Projection: For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Creating Wireframe Geometry: Creating Projections.
- Create Join: Joins surfaces or curves. See Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Performing Operations on Shape Geometry: Joining Surfaces or Curves.
- Create Extrapol: Extrapolates surface boundaries or curves. For more information, see Generative Shape Design User's Guide: Performing Operations on Shape Geometry: Extrapolating Surfaces and Extrapolating Curves.
- You can create limiting elements just by clicking on the edge to be filleted. The application displays this element as a blue disk.
- You can select points as limiting elements. These points must be located on the edge to be filleted and they must have been created using the 'On curve' option available in the Point Definition dialog box.
![]()
Variable Radius Fillets Using Closed Edges
- The application defines a default point on closed edges when applying the Variable Radius Fillet command. To define your fillet, first of all you need to remove this point, and then use 3D points or planes only.
- The Linear propagation mode is not valid for closed edges and edges continuous in tangency.