Effect of Reverse Machining Conditions | |||||
|
| ||||
| Machining Operation | Effect of Reverse Machining Conditions |
| Prismatic Roughing | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Profile Contouring | Climb and Conventional options are inverted
Order of multi-contours is inverted. Start and End elements, offsets are inverted |
| Facing | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Pocketing | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Plunge Milling | Nothing to reverse |
| 4-Axis Pocketing | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| All Axial Maching Operations | Order of pattern points is inverted |
| Tslotting | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Circular Milling | Climb and Conventional options are inverted Order of pattern points is inverted |
| Sequential Axial | Order of pattern points is inverted |
| Slot Milling | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Groove Milling | Climb and Conventional options are inverted Inversion of Geometry points |
| Sequential Groove | Climb and Conventional options are inverted for circular and helical motion |
| Thread Milling | Order of pattern points is inverted |
| CUTCOM | You should check that the desired cutter compensation is still applied (correct side, and so on). |
| Roughing | Climb and Conventional options are inverted. |
| Cavities Roughing | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Sweep Roughing | Start direction is inverted |
| Power Machining | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Advanced Finishing | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Contour Driven | Tool Path is inverted |
| 4-Axis Curve Sweeping | Start direction is inverted |
| Sweeping | Tool Path is inverted |
| Pencil Machining | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Zlevel | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Spiral Milling | Climb and Conventional options are inverted. |
| Isoparamametric machining Operations | Order of parts is inverted. Corners 1 and 2 are swapped. Corners 3 and 4 are swapped. Corresponding interpolation axes at corners are swapped. |
| Multi-Axis Isoparametric Machining | Pole points are inverted |
| Multi-Axis Sweeping | Start direction is inverted |
| Multi-Axis Contour Driven | Start direction is inverted |
| Multi-Axis Spiral Milling | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Multi-Axis Tube Machining | Way of cut (clockwise/counter) is inverted |
| Multi-Axis Helix machining | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Multi-Axis Curve Machining | Climb and Conventional options are inverted Geometry points are inverted Sign of Tilt angle is changed to invert the left/right condition Couple of Points limit elements are swapped.For Tangent Axis guidance along isoparametric lines: when machining a strip of drive surfaces, check that the reference tool axis gives the desired result for the best matching u or v isoparametric line of the first machined face. |
| Multi-Pockets Flank Contouring | Climb and Conventional options are inverted |
| Multi-Axis Flank Contouring | Geometry parameters are inverted |
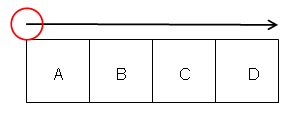
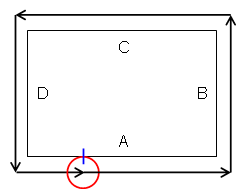
| Multi-axis Flank Contouring | Climb and Conventional options are inverted Order of drives is inverted as follows when the
Close tool path check box is not selected.
Drives A, B, C, D are machined in the order D, C, B, A.
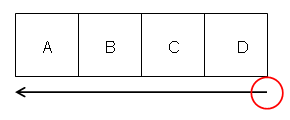
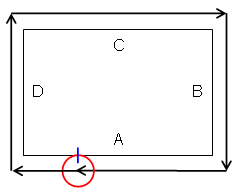
Order of drives is inverted as follows when the Close tool
path check box is selected.
Drives A, B, C, D are machined in the order A, D, C, B, A.
Drive A is the first and last machined element.
Start and End elements, offsets, and conditions are inverted. Approach and Leave distances are swapped. Manual direction is inverted (Left / Right). Local stopping condition and Local restarting direction are updated. |