About Speed and Acceleration Probes | |||||
|
| ||||
Key terms
Speed, velocity, acceleration, and instantaneous center of rotation play a prominent role in speed and acceleration probes and need to be defined more accurately.
- Speed
- The rate of motion, or the rate of change of position. It is expressed as distance moved (d) per unit of time (t). Speed is a scalar quantity with dimensions d/t. Speed is measured in the same physical units of measurement as velocity but does not contain an element of direction. Speed is thus the magnitude component of velocity.
- Velocity
- The rate at which the object changes its position. Velocity is a vector value that contains both magnitude and direction components. Velocity is measured in the same physical units of measurement as speed with d/t dimensions.
- Acceleration
- The rate of change of velocity. It is thus a vector quantity with dimensions d/(t2). To accelerate an object is to change its velocity, which is accomplished by altering either its speed or direction (as in the case of uniform circular motion) in relation to time.
- Instantaneous Center of Rotation
- The point about which a body is rotating at any given instant.The figures below consider two particles, A and B, in a body.
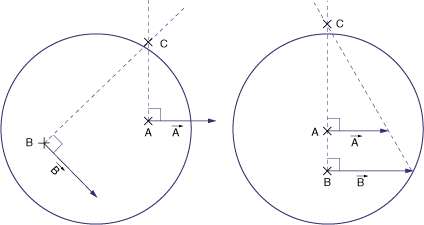
- In the left figure, the velocities of A and B are known and different; the position of the ICR is obtained by drawing the perpendicular to Velocity A through A and the perpendicular to Velocity B through B; the point in which these two lines intersect is the intantaneous center of rotation.
- In the right figure, the velocities of A and B are perpendicular to the AB line and their magnitudes are known; the instantaneous center of rotation is the point at which AB line intersects with the line joining the extremities of the vector.
![]()
Speed and Acceleration Probe Definition
Speed and accelerations of a specified point with X, Y, and Z components are calculated with respect to a reference product along an axis system.
Two types of speed and accelerations can be measured with the Speed and Acceleration probe:
- Linear speed and acceleration of a specified point with respect to a reference product.
- Angular speed and acceleration calculations of the product to which the point belongs.
The result of the probe with X, Y, and Z components are calculated with respect to the axis system of the main product or another axis system defined by the user.
Result of the Probe
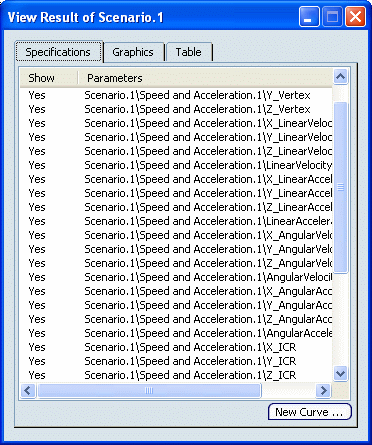
The table below summarizes the result values of the speed and acceleration probe that are listed in the Probe Result Display dialog box.
| Point Coordinates | X_"PointName": X coordinate of computation point |
Y_"PointName": Y coordinate of computation point |
|
Z_"PointName": Z coordinate of computation point |
|
| Angular Velocity Coordinates | X_AngularVelocity: X projection of angular velocity |
Y_AngularVelocity: Y projection of angular velocity |
|
Z_AngularVelocity: Z projection of angular velocity |
|
AngularVelocity: magnitude of angular velocity |
|
| Angular Acceleration Coordinates | X_AngularAcceleration: X projection of angular acceleration |
Y_AngularAcceleration: Y projection of angular acceleration |
|
Z_AngularAcceleration: Z projection of angular acceleration |
|
AngularAcceleration: magnitude of angular acceleration |
|
| Linear Velocity Coordinates | X_LinearVelocity: X projection of linear velocity |
Y_LinearVelocity: Y projection of linear velocity |
|
| Z_LinearVelocity: Z projection of linear velocity |
|
LinearVelocity: magnitude of linear velocity |
|
| Linear Acceleration Coordinates | X_LinearAcceleration: X projection of linear acceleration |
Y_LinearAcceleration: Y projection of linear acceleration |
|
Z_LinearAcceleration: Z projection of linear acceleration |
|
LinearAcceleration: magnitude of linear acceleration |
|
| Instant Center of Rotation Coordinates | X_ICR: X coordinate of the instant center of rotation |
Y_ICR: Y coordinate of instant center of rotation |
|
Z_ICR: Y coordinate of instant center of rotation |
Here is an example of a speed and acceleration result: