In the Shape Analysis toolbar, click Connect Checker Analysis
 .
.
The Connect Checker dialog box is displayed.
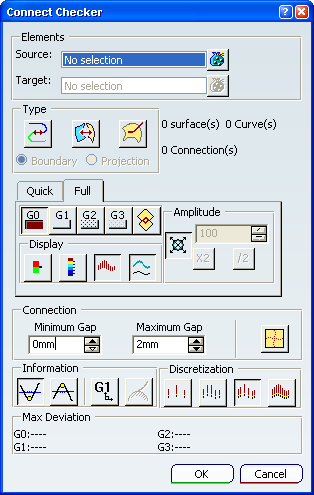
In the Type area of the dialog box, select the type of connection you want to check.
- Curve-Curve Connection
- Surface-Surface Connection

- Surface-Curve Connection
Note:
If you select one of these connection types the analysis will be done in Implicit Mode. If you do not make a selection, the analysis will be done in Explicit Mode.
In this example, Surface-Surface Connection  is selected because we are analyzing only the connection between two surfaces.
is selected because we are analyzing only the connection between two surfaces.
Select one or several elements by doing one of the following:
- To select a single element:
- Click the element in the 3D area or in the specification tree.
- To select multiple elements using Ctrl-click:
- Ctrl-click each of the elements in the 3D area or in the specification tree.
- When finished, press F8.
- To select multiple elements using the Elements / Objects dialog box:
- Click
 next to the Elements / Objects selection box.
next to the Elements / Objects selection box. The dialog box opens.
- Click the elements in the 3D area or in the specification tree to add them to the list in the dialog box.
- If necessary, Remove or Replace elements.
- When finished, click Close.
The element name or the number of selected elements is shown in the Elements / Objects selection box.
In the dialog box, click the Quick tab.
Quick analysis provides a simple visual indication of connections which exceed the Threshold values for each selected continuity analysis type.
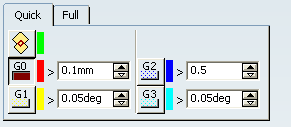
In the Quick tab, select the continuity analysis type to display:
- Overlap Defect : overlapping elements (selecting this disables the other analysis types)
- G0 continuity : continuity in point
- G1 continuity : continuity in tangency
- G2 continuity : continuity in curvature
- G3 continuity : continuity in hedgehog curvature
Note:
Depending upon your selection in the Type area of the dialog box, you may be able to select more than one analysis type.
In this example, G0 continuity is selected.
The visual representation of the analysis appears on the elements.
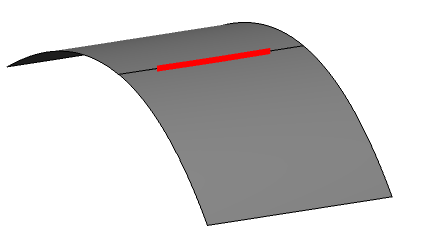
In the example, the thick red line indicates all points that are
separated by a gap which exceeds the Threshold value for G0 continuity, which in this example is set at 0.1 mm.
The Max Deviation area at the bottom of the dialog box displays the maximum values of the G0, G1, G2 and G3 continuities.
Optional: In the Quick tab, use the spin boxes to adjust the Threshold values.
The visual representation of the analysis is updated.
Optional: If you are analyzing elements which have been joined (using a join or match command) and you want to analyze the internal connections, select Internal Edge
 (this command is by default unselected).
(this command is by default unselected).
In the dialog box, click the Full tab and then select Comb  and Envelope
and Envelope  .
.
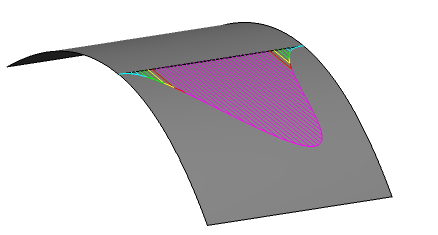
The thick red line of the Quick analysis is replaced by a comb of spikes bounded by an envelope.
The color of a spike indicates whether the connection at the position of the spike is below the Threshold value and the length of the spike indicates the magnitude of the discontinuity.
In the Information area of the dialog box, select MinInfo  and MaxInfo
and MaxInfo  .
.
The minimum
and maximum values of the analysis are displayed on the element.
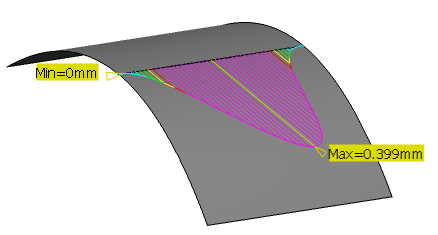
Optional: In the Connection area of the dialog box, adjust the values of Minimum Gap and Maximum Gap.
The Connect Checker Analysis command measures the gap of all the connections between all the borders of the geometrical elements, irrespective of the size of the geometrical elements.
- If the value of the gap is greater than Minimum Gap and less than Maximum Gap, the connection is analyzed.
- If the value of the gap is outside of these limits, the connection is not analyzed.
The visual representation of the analysis is updated.
Adjust the analysis color scale on the element:
- In the Display area of the dialog box, select Full Color Scale
 .
.
The Connect Checker Analysis color scale dialog box is displayed.
- In the color scale dialog box, select the
Auto Min Max check box.
- The maximum and minimum values in the dialog box are set according to the values detected on the element.
- The analysis colors are updated to match the color scale in the dialog box.
When you have finished working with this command, do one of the following:
- To create the analysis, click OK.
The analysis is added to the specification tree where it is identified as Command_Name.Analysis.x.
The analysis will be updated automatically whenever you modify any of the elements in the analysis (for example when you deform an element using control points).
- To abandon the analysis, click Cancel.