Click Sketch Analysis
 in the Tools toolbar (2D Analysis Tools sub-toolbar).
in the Tools toolbar (2D Analysis Tools sub-toolbar).
The Sketch Analysis dialog box appears. It contains three
tabs: Geometry, Projections / Intersections and
Diagnostic.
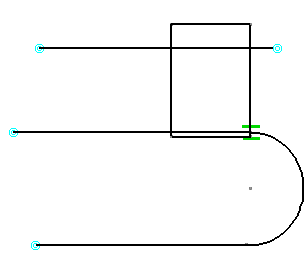
Note that some geometrical items and constraints are highlighted
so that you can see them easily.
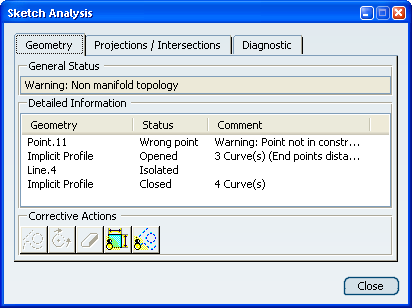
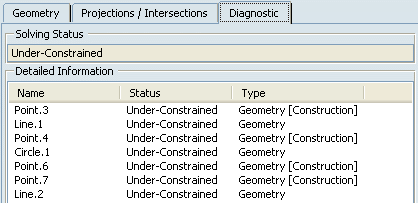
The Geometry tab displays information helping
you know whether the sketch geometry is valid. In the Detailed
Information table, select an item.
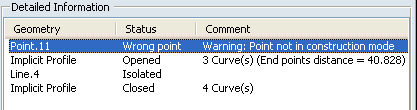
Click the Set in Construction mode icon to
turn the standard mode point into a construction mode point and solve
the problem.
Select the Diagnostic tab.
The information on this tab displays a full
diagnosis of a sketch geometry. It provides a global analysis
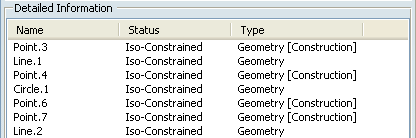
of the sketch as a whole, and specifies whether individual geometrical
elements in the sketch are under-constrained (under-defined),
over-constrained (over-defined) or iso-constrained (well defined):
Close the Sketch Analysis dialog box.
Right-click the Point.xxx item in the sketch or from
the specification tree and select Point.xxx object > Fix.
Repeat this operation for the other items.
Re-open the Sketch Analysis dialog box and
select the Diagnostic tab.
You can notice that the items you fixed are now iso-constrained.