Click Translate
 in the Operation toolbar (Transformation sub-toolbar).
in the Operation toolbar (Transformation sub-toolbar).
The Translation Definition dialog box appears.
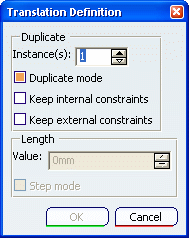
In the Instances field, keep 1 as the number
of instances to be created.
Keep Duplicate mode selected.
The Duplicate mode option is activated by default, which
means that the 2D elements you select will be copied. If you clear
Duplicate mode, the element will be moved.
Select Keep internal constraints.
This option specifies that you want to preserve in the translation the
internal constraints applied to the selected elements.
Keep Keep external constraints deactivated.
Any external constraint existing between the selected elements and external
elements will be disregarded in the translation.
Select the elements to be translated using the trap
selection.
You may either select one 2D element, or multi-select the entire 2D
geometry by trapping it with the mouse as shown below.
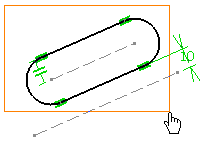
Click to indicate the translation vector starting point.
You can define the translation length in the geometry area, using the
mouse. For more precise results, enter a specific value for the translation
length in the Translation Definition dialog box.
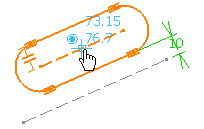
Type 30mm in the length field and press
Enter.
Click to indicate the translation vector ending point.
Click OK.
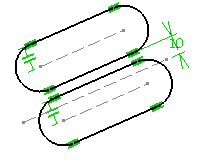
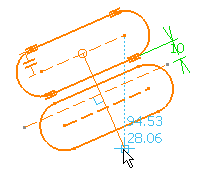
The translation has been performed. You can notice that the internal
constraints were preserved in the translated element (four tangency
constraints, and a parallelism constraint), whereas the external constraint
(an offset constraint) was not.