In the Activities Process Tree, select the tool path and place the cursor in the Computed column.
- Right-click the tool path to display the
contextual menu providing tool path edition commands.
- Select Check Tool Length
 .
. A dialog box is displayed.
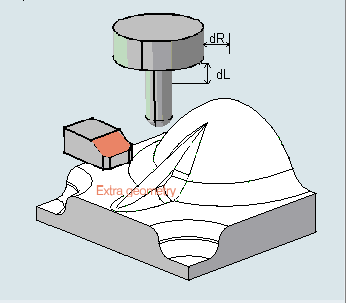
Click Extra geometry to add additional geometry to the part
in the Machining Operation where the tool path was computed.
Additional geometry may be a face or a clamp that you would rather
avoid using in the computation and
that is not defined in the
Machining Operation.
Set the other parameters:
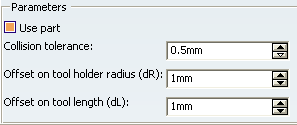
- When you select Use part, the part you defined in
the Machining Operation is used to compute the collision points.
- Collision tolerance defines the distance within
which the tool holder is considered to be in collision.
- Offset on tool holder radius and Offset on
tool length define the tolerance distances specific
to the tool holder radius and tool length.
Click Apply.
- The tool path is displayed on the
part.
The points where the tool holder is in collision with the part are shown
in red.
-
A small dialog box is displayed that gives the number of collision
points on this tool path,
the minimum tool length that is required in order to avoid having
collision points and
the coordinates of the current point
(move the mouse over the tool path to see the coordinates change for
each point)
plus reference data on the tool length and the offset on the tool
length.
You can also display the tool on the tool path.
Click Cancel to close the dialog box.
- This is only a visual check to let you see where the collision points
are and
find the tool length that is required to avoid them.
- If a tool holder is defined, the dialog box displays information
on the tool gage.
- You now have
the choice of either changing the tool length or
editing the tool path in order to get rid of the collision points.
If you want to change the tool length you must create a new tool or select
another tool.
Select the tool path again in the Activities Process Tree.
Choose Area modification in the contextual menu.
The tool path
is displayed.
Click Select collision points
 .
.
The same dialog box as above is displayed.
Change the parameter values if
you wish.
Click Apply to display the collision points in
red on the tool path.
Cut ( )
the collision points from the tool path.
)
the collision points from the tool path.