Assemble Product
You can build a NC resource using components that have already been created,
that is, assemble existing parts within the product structure. This is done in the Assembly Design workbench.
Click
 , to enter the Assembly Design workbench.
, to enter the Assembly Design workbench. Right-click Product node, and select
The Select products to insert dialog
box appears.
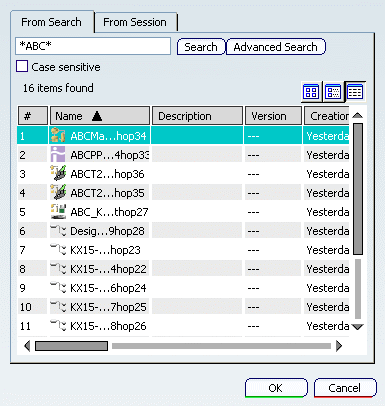
Search for the desired part, and open it. The inserted part appears in the resource tree and in
the graphical view. Repeat these steps to insert all the required parts. See About Defining Machine Kinematics

Position the Inserted Parts
You can position the components correctly.
Right-click compass and select Snap Automatically
to Selected Object.

Select the Part in the resource tree.
The compass snaps
to this component in the graphics area.
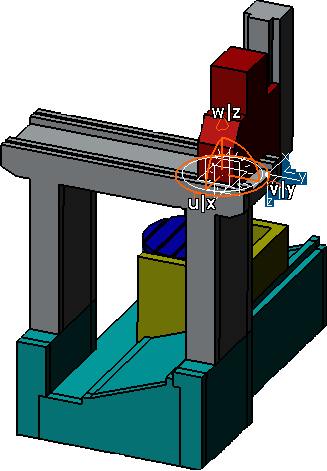
Click Part and drag it to the right position.
Alternatively, right-click the compass attached
to the part, and select the Edit command.
The Parameters for Robot Manipulation
dialog box appears; Enter the desired values, and then click
Apply to effect the position on the selected component.
Repeat the above steps for each of the components, to
position them correctly.

Create Engineering Connections
You can create Engineering
Connections after inserting the products. You must create Engineering
Connections to fix these products to the NC resource, using the Assembly Design workbench. The supported engineering
connections are Revolute, Prismatic, and Rigid. The Fixed Engineering Connection must be defined along with other engineering
connections. It is mandatory to create a Fixed Engineering Connection. Fixed part is the one which does not move. When modeling controlled machines, it is
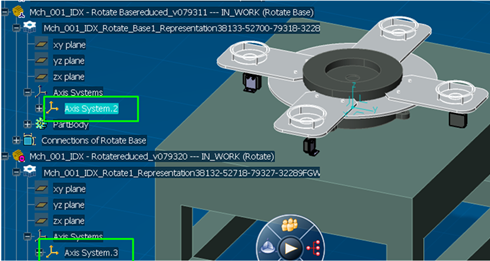
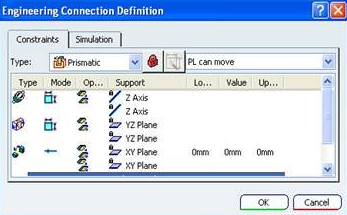
recommended to use the CATIA Axis Systems to define the joints
that comprises the controlled degrees of freedom. This allows
for a repeatable and consistent definition of joint zero position
and joint motion positive direction. These best practices should be applied
for all those engineering connections created through FBDI whose
directions do not match with corresponding V5 joint
directions.
For Rotational Joint - For Type, select Revolute, followed by second can move.
- Right-click and select .
- Set the Coincidence by first selecting the Z Axis of the Parent followed by the Z Axis of the Child.
The part which can move is referred to as the Child, and the other part with respect to which it moves is referred to as the Parent. Each part should have an Axis System defined such that the Z axis of the system is along the rotational Joint direction and the two Axis Systems are coincident on top of each other when the Joint is in its zero position.
- Set the Mode to Driving and Option to Same.
- Right-click and select .
- Set the Contact by first selecting the XY Plane of the Parent and then the XY Plane of the Child.
- Set the Mode to Driving and Option to Same.
- Right-click and select .
- Set the Angle by first selecting the YZ Plane of the Parent and then the YZ Plane of the Child.
- Set the Mode to be Controlled
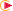 By default,
its value is 0 degree.
By default,
its value is 0 degree.
For Translational Joint - For Type, select Prismatic, followed by second can move.
- Right-click and select .
- Set the Coincidence by first selecting the Z Axis of the Parent followed by the Z Axis of the Child.
The part which can move is referred to as the Child, and the other part with respect to which it moves is referred to as the Parent. Each part should have an Axis System defined such that the Z axis of the system is along the translational Joint direction and the two Axis Systems are coincident on top of each other when the Joint is in its zero position.
- Set the Mode to Driving and Option to Same.
- Right-click and select .
- Set the Contact by first selecting the YZ Plane of the Parent and then the YZ Plane of the Child.
- Set the Mode to Driving and Option to Same.
- Right-click and select .
- Set the Offset by first selecting the XY Plane of the Parent and then the XY Plane of the Child.
- Set the Mode to be Controlled, and mode to Same.
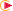 By default,
its value is 0 degree.
By default,
its value is 0 degree.
An offset can also be added along with the lower and/or upper limit.

Create a Mechanism
You can create Mechanism in NC resource.
Enter the workbench. In order to complete the NC resource definition, you
must:
- Create a mechanism using the workbench. Interchangeable milling heads, turrets, spindles etc. are separate NC resources and they have to have their own mechanism.
- Include specific engineering connections, previously created in
the Assembly Design workbench, in the mechanism.
Select the root node of the product tree, then click Create a New Mechanism in the Mechanism Edition toolbar. in the Mechanism Edition toolbar. The Mechanism/Representation definition dialog box appears.
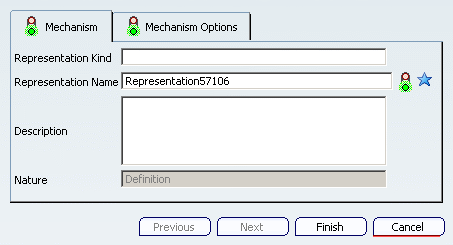
Name the representation as required, then click Finish to create the new representation. A new mechanism representation is created under the product, and
all engineering connections from the product are included as joints
and commands by default.
Note:
Interchangeable milling heads, turrets, spindles etc. are separate NC resources and they have their own mechanism.

Also See . Click Kinematics Simulation  to open Mechanism Player dialog box. to open Mechanism Player dialog box. In Mechanism Player you can assign upper and lower limits to the command values in a
mechanism. See . You are now ready to create a NC Resource. See Creating a NC Resource.
|
![]()








