Two limits
You can create
swept surfaces that use an implicit linear profile by defining two guide curves and limits to each guide.
Click Sweep
 . .
The Swept Surface Definition dialog box appears.
Click the Line profile icon and select
Two Limits from the Subtype list.
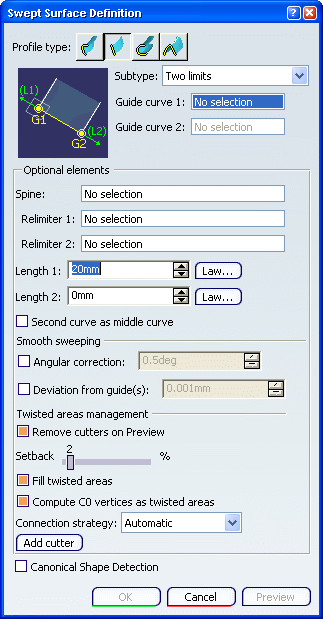
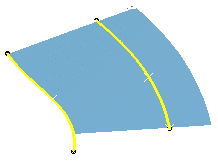
Select two guide curves. You can enter one or two length values to define the
width of the swept surface.
If needed, select a Spine to specify a spine
different from the first guide curve.
If no spine is selected, the guide curve is implicitly used as the spine.
If the plane normal to the spine intersects one of the guiding curves at
different points, it is advised to use the closest point to the spine
point for coupling. Click OK to create the swept surface. The surface (identified as Sweep.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

Limit and middle
You can create
swept surfaces that use an implicit linear profile by defining the limits and using second curve as middle curve.
Click Sweep
 . .
The Swept Surface Definition dialog box appears.
Click the Line profile icon and select
Limit and Middle from the Subtype list.
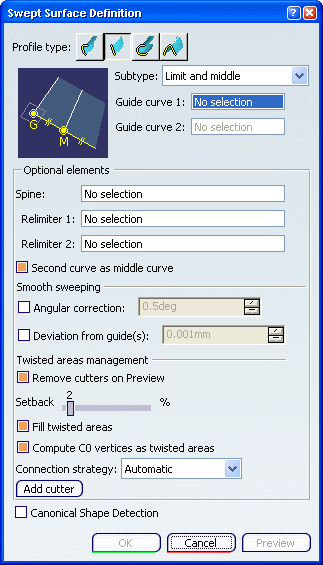
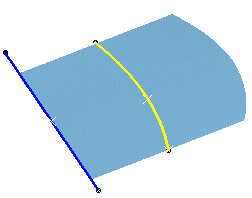
Select two guide curves. Select the Second curve as middle curve check
box to use the
second guide curve as the middle curve.
If needed, select a Spine to specify a spine
different from the first guide curve.
If no spine is selected, the guide curve is implicitly used as the spine.
If the plane normal to the spine intersects one of the guiding curves at
different points, it is advised to use the closest point to the spine
point for coupling. Click OK to create the swept surface. The surface (identified as Sweep.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

With reference surface
You can create
swept surfaces that use an implicit linear profile by defining reference surface.
Click Sweep
 . .
The Swept Surface Definition dialog box appears.
Click the Line profile icon and select
With reference surface from the Subtype list.
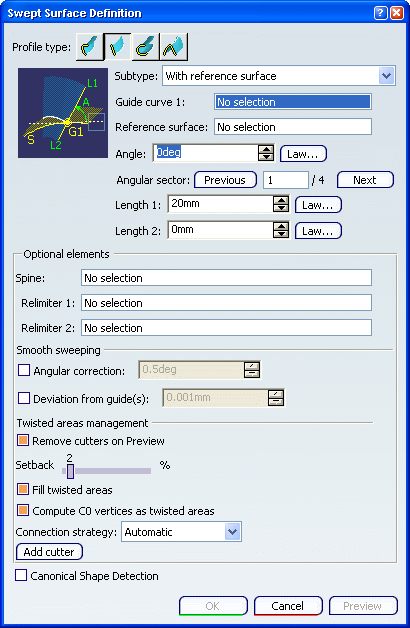
Select a guide curve, a reference surface and key in an
angle value.
You can enter one or two length values to define the
width of the swept surface.
If needed, select a Spine to specify a spine
different from the first guide curve.
If no spine is selected, the guide curve is implicitly used as the spine.
If the plane normal to the spine intersects one of the guiding curves at
different points, it is advised to use the closest point to the spine
point for coupling. Click OK to create the swept surface. The surface (identified as Sweep.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

With reference curve
You can create
swept surfaces that use an implicit linear profile by defining reference curve.
Click Sweep
 . .
The Swept Surface Definition dialog box appears.
Click the Line profile icon and select
With reference curve from the Subtype list.
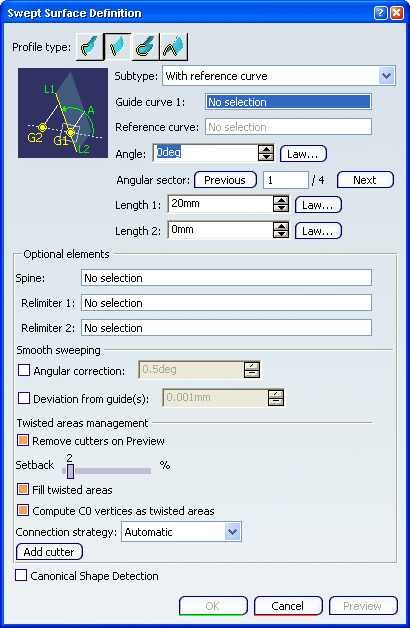
Select a guide curve, a reference curve, and key in an
angle value. You can enter one or two length values to define the
width of the swept surface.
If needed, select a Spine to specify a spine
different from the first guide curve.
If no spine is selected, the guide curve is implicitly used as the spine.
If the plane normal to the spine intersects one of the guiding curves at
different points, it is advised to use the closest point to the spine
point for coupling. Click OK to create the swept surface. The surface (identified as Sweep.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

With tangency surface
You can create
swept surfaces that use an implicit linear profile by defining the tangency surface.
Click Sweep
 . .
The Swept Surface Definition dialog box appears.
Click the Line profile icon and select
With tangency surface from the Subtype list.
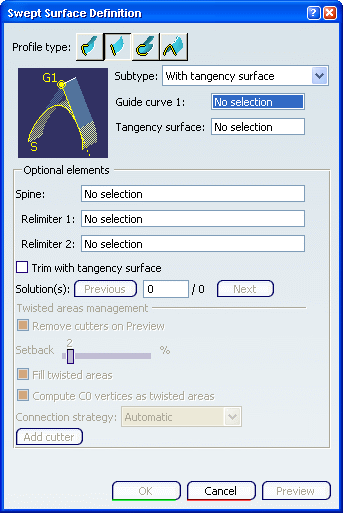
Select a guide curve, and a reference surface to which
the sweep is to be tangent. Depending on the geometry, there may be one or two
solutions from which to choose, either by clicking on the solution
displayed in red (inactive), using the Previous or Next
buttons or entering a solution number in the Solution(s)
field. You can select the Trim with
tangency surface check box to perform a trim between the swept surface and
the tangency surface. The portion of the tangency surface that is kept is
chosen so that the final result is tangent. Two solutions
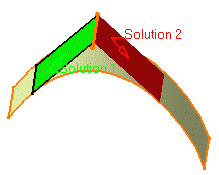
Choosing solution 2
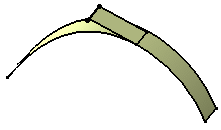
Choosing solution 2 with Trim option
If needed, select a Spine to specify a spine
different from the first guide curve.
If no spine is selected, the guide curve is implicitly used as the spine.
If the plane normal to the spine intersects one of the guiding curves at
different points, it is advised to use the closest point to the spine
point for coupling. Click OK to create the swept surface. The surface (identified as Sweep.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

With draft direction
You can create
swept surfaces that use an implicit linear profile by defining draft direction.
Click Sweep
 . .
The Swept Surface Definition dialog box appears.
Click the Line profile icon and select
With draft direction from the Subtype list.
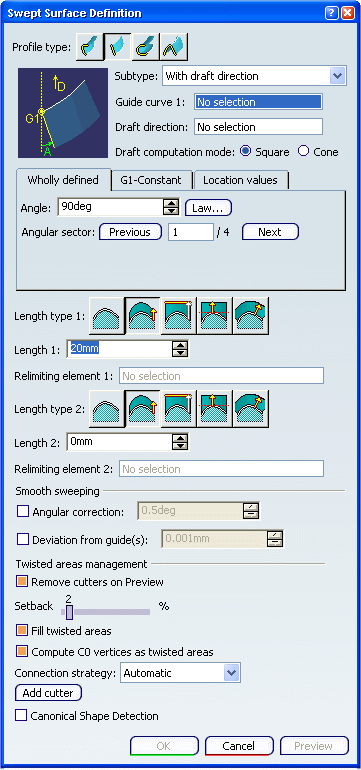
Select a guide curve and a draft direction (a line, a
plane or components). Select the draft computation mode:
-
Square:
equivalent to implicit linear profile swept surface with reference
surface, using a plane normal to the draft direction as reference
surface, and the projection of the guide curve onto this plane as
spine.
-
Cone:
envelop of cones defined along a given curve. In order to have
swept start and end planes similar as the square mode, the guide
curve needs to be extrapolated and the resulting surface split as
explained in the following figure.
-
Choose the
angular definition:
-
Wholly defined: the angular value varies during the whole
sweeping operation
-
G1-Constant: a different draft value for every G1 section
can be set; in this case, a relimiting plane is requested when
defining lengths
-
Location values: on given points on the curve, angular
values can be defined.
Choose the length types:
- From curve: the swept surface starts from the curve
- Standard: the length is computed in sweeping planes
(defining 0 is similar as choosing From curve)
- From/Up to: the length is computed by intersecting a
plane or a surface; a point can be selected: a plane parallel to
the draft plane would be computed
- From extremum: the lengths are defined along the
draft direction from an extremum plane; L1 corresponds to the
"maximum plane" in the draft direction, L2 corresponds to the
"minimum plane" in the draft direction
- Along surface: the length is used as the distance of
an Euclidean parallel curve to relimit the swept surface
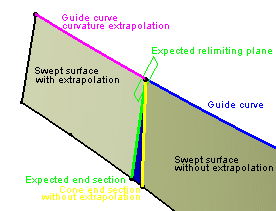
The start (or end) section of the swept surface (in
yellow) does not coincide with the expected relimiting plane (in
green). As a consequence, the blue portion needed is missing. Here
are the steps performed to create the swept surface.
As an information purpose, we put all the elements explaining the
steps above in Geometrical Set.2, so that you understand how the
sweep surface is created.
- The guide curve is extrapolated in curvature (pink curve)
- The result is split by the green plane to obtain the green end
section.
Click OK to create the swept surface. The surface (identified as Sweep.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

With two tangency surfaces
You can create
swept surfaces that use an implicit linear profile by defining two tangency surfaces.
Click Sweep
 . .
The Swept Surface Definition dialog box appears.
Click the Line profile icon and select
With two tangency surfaces from the Subtype list.
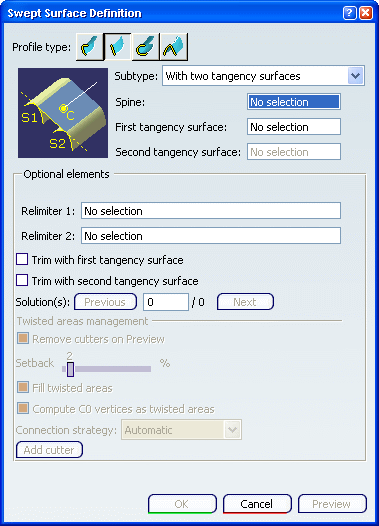
Select a spine, and two tangency surfaces. You can select the Trim with tangency surface
check box
to perform a trim between the swept surface and the tangency surface. The
portion of the tangency surface that is kept is chosen so that the final
result is tangent. Swept surface without trim
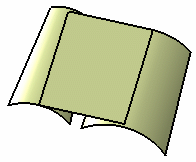
Trim with both surfaces
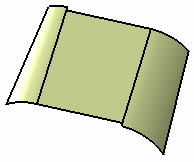
Trim with first tangency surface
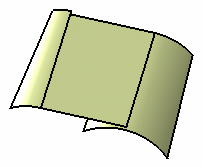
Trim with second tangency surface
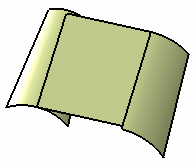
If needed, select a Spine to specify a spine
different from the first guide curve.
If no spine is selected, the guide curve is implicitly used as the spine.
If the plane normal to the spine intersects one of the guiding curves at
different points, it is advised to use the closest point to the spine
point for coupling. Click OK to create the swept surface. The surface (identified as Sweep.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

Preview the Angular Value
You can preview the various solutions you will get after completion of the command.
When creating a sweep, you are now able to preview
the four solutions based on the values given for the Angle and
Lengths. The first solution corresponds to Angle, Length1 and
Length2 values, the second solution to - Angle, Length1 and Length2
values, the third solution to Angle, Length2 and Length1 values, and
the fourth solution to -Angle, Length2 and Length1 values.
- Use the spinners to define an Angle.
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



















