Extrapolating Surfaces | |||||
|
| ||||
The Extrapolate Definition dialog box appears.
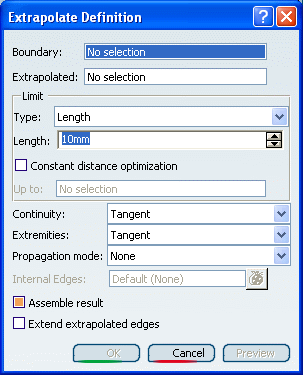
Select a surface Boundary.
Select the surface to be Extrapolated.
Select the extrapolation Type:
-
Length: enter the value in the Length field or use the manipulators in the 3D geometry.
Warning: It is not advised to enter a negative value in the Length field. -
Up to: the Up to field is enabled. Select an element belonging to the same support as the surface to be extrapolated (surface or plane).
Warning: This option is only available with the Tangent continuity type.
-
Specify the Limit of the extrapolation by either:
-
entering the value of the extrapolation length
-
selecting a limit surface or plane
-
using the manipulators in the geometry.
-
Specify the Continuity type:
- Tangent: the extrapolation side is tangent to the extrapolated surface tangent
- Curvature: the extrapolation side complies with the curvature of the side of the extrapolated surface.
Tangent continuity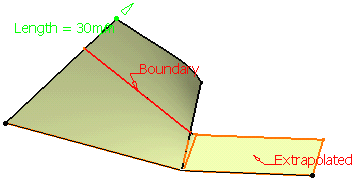 Curvature continuity
Curvature continuity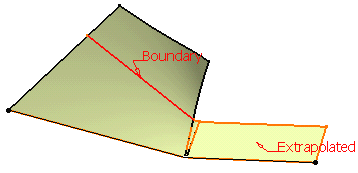
Specify Extremities conditions between the extrapolated surface and the support surface.
- Tangent: the extrapolation sides are tangent to the edges adjacent to the surface boundary.
- Normal: the extrapolation sides are normal to the original surface boundary.
Tangent extremity (and tangent continuity) Normal extremity (and curvature continuity)
Normal extremity (and curvature continuity)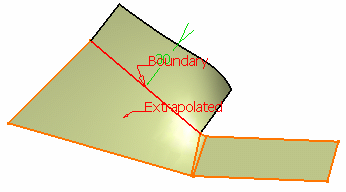
Specify the Propagation type:
- Tangency continuity to propagate the extrapolation to the boundary's adjacent edges.
- Point continuity to propagate the extrapolation around all the boundary's vertices.
Tangent continuity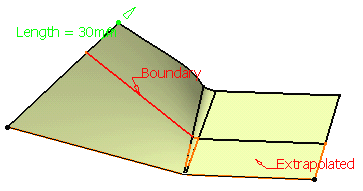 Point continuity
Point continuity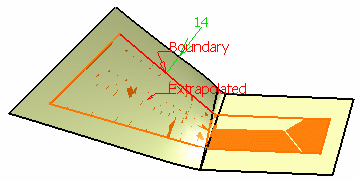
Click OK to create the extrapolated surface.
The surface (identified as Extrapol.xxx) is added to the specification tree.