Create an Edge Fillet
You can define fillet by selecting edges.
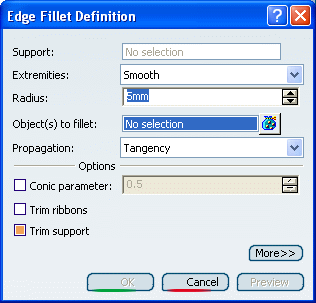
Click Edge Fillet
 . .
The Edge Fillet Definition dialog box appears.
Select the edge to be filleted.
You can also select a face, provided there is no
ambiguity as to the edge(s) to be filleted.
Use the combo to select the desired type of extremity for
the fillet:
-
Straight: no tangency constraint is
imposed at the connecting point between the fillet and the initial
support, generating sometimes a sharp angle
- Smooth: a tangency constraint is imposed at
the connection between the fillet surface and the support surfaces,
thus smoothing the connection
- Maximum: the fillet surface is limited by the
longest selected edge
- Minimum: the fillet surface is limited by the
shortest selected edge
(Refer to
Creating
Shape Fillets)
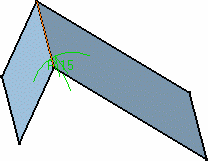
Enter the value of the fillet Radius.
A preview of the fillet appears.
You can choose the Propagation type:
-
Tangency: the fillet is propagated up to the first edge that
is not continuous in tangency.
The tangent continuous edges of the selected edge are managed to ensure a better fillet stability and robustness (More fillets are automatically rerouted in case of design changes). Note:
If the Tangent Intersection edges activation icon is selected in
the User Selection Filter toolbar, the Tangency mode is selected by default in the Edge Fillet Definition dialog box. For further information, refer to
CATIA Infrastructure User's Guide : Selecting Using a Filter.
-
Minimal: the fillet is propagated up to the first geometric
limitation.
-
Intersection: the fillet is
propagated to all the edges that have been generated by
intersecting the features.
Note:
If the Intersection edges activation icon is selected in
the User Selection Filter toolbar, the Selection mode automatically switches to Intersection in the Edge Fillet Definition dialog box. For further information, refer to
CATIA Infrastructure User's Guide : Selecting Using a Filter.
Select the Conic parameter
check box. This check box allows you to vary the section of the fillet.
You can select the Trim support check box to relimit
the support elements and assemble them to the fillet. Click OK to create the fillet surface.
The surface (identified as EdgeFillet.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

Trim Overlapping Fillets
In some cases, fillets may be overlapping.
The Trim ribbons option lets you solve this by trimming the
fillets where they overlapping.
Click Edge Fillet
 and select the edges at the base of the
cylinder and the one along the vertical surface.
and select the edges at the base of the
cylinder and the one along the vertical surface.
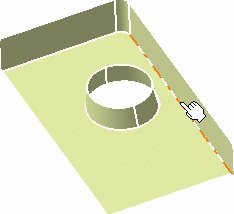
Click Preview.
The two fillets clearly overlap:
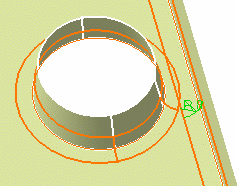
Select the Trim
ribbons check box and click OK.
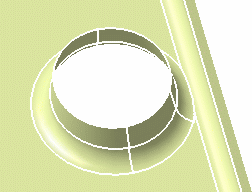
Note that the Trim ribbons option is enabled with the
Tangency and Intersection edges propagation modes:
- In Minimal mode, the Trim ribbons option is grayed
out,
as it is implicitly active. The results would be trimmed fillets,
and no propagation.
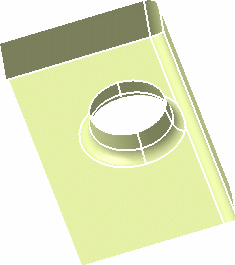
- In Tangency mode, with the Trim ribbons
option
cleared, the fillets intersect, with no trimming, and the
propagation is performed.
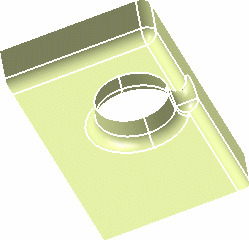
- In Tangency mode, with the Trim ribbons
option selected, the fillets are trimmed and the propagation is performed.
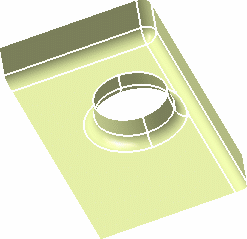

Keep Edges
You may also need to explicitly indicate edges that should
not be filleted, if a radius is too large for example.
In this case, you
cannot select boundary edges to be kept, but only internal edges, i.e.
edges limiting two faces.
Once
the edge to be filleted has been selected, click
Preview then
More>>.
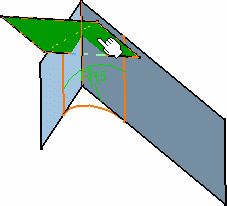
Select the edge(s) you wish to keep in the Edge(s) to keep field.

If you have difficulties
selecting the edge, use the up/down arrows to display the preselection
navigator.
CATIA displays this edge in pink, meaning
that it will not be affected by the fillet operation.
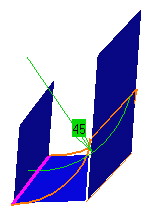

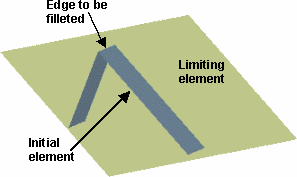
Limit Fillets
While creating the fillet, you can limit it by selecting a surface that
intersects it completely.
Click in the Limiting
element(s)
field and select the trimming element(s).

These elements can either be surfaces, planes, or points on edges. An arrow indicates which portion of the fillet is to
be retained.
Click on this arrow to inverse it, if needed, to retain
the opposite side of the fillet.
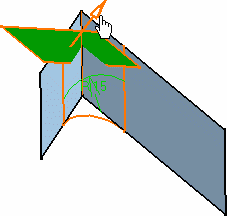
Click OK to
create the limited fillet.
In the illustration, the limiting surface has been hidden.
You can create limiting elements just
by clicking on the edge to be filleted. The application displays this element as a blue disk.
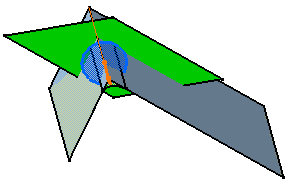

Fillet Volumes
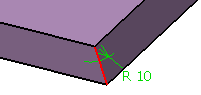
You can fillet the edges of the volumes.
Click Edge Fillet
 . .
The Edge Fillet Definition dialog box appears.
Select the edge of the volume to be filleted. Set the Radius to 10mm.
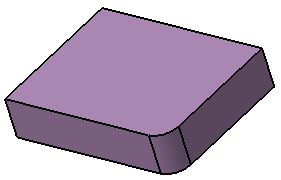
Click OK to create the fillet volume.
|
![]()
![]()