Creating Points | |||
| |||
A button ![]() is available besides the Point type to prevent an
automatic change of the type while selecting the geometry. Click it so that the lock turns red
is available besides the Point type to prevent an
automatic change of the type while selecting the geometry. Click it so that the lock turns red ![]() .
For instance, if you select the On Curve type, you are
not able to select a line. If you want to select a line, choose
another type in the list. The status of this button is stored as the default value: therefore, if it is red and you launch the same command again or another command owning this button, the button will be red too.
.
For instance, if you select the On Curve type, you are
not able to select a line. If you want to select a line, choose
another type in the list. The status of this button is stored as the default value: therefore, if it is red and you launch the same command again or another command owning this button, the button will be red too.
Create a Point Using Coordinates
You can create a point by defining the coordinates from reference point.
The Point Definition dialog box appears.
In the Point type list, select the Coordinates point type.
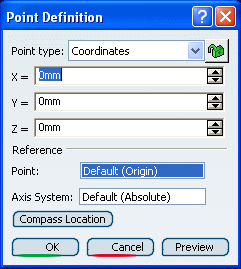
Enter the X, Y, Z coordinates in the current axis-system.
Optional: In the Point box, select a reference point.
When the command is launched at creation, the initial value in the Axis System box is the current local axis system. If no local axis system is current, the box is set to Default.
Whenever you select a local axis system, the point's coordinates are changed with respect to the selected axis system so that the location of the point is not changed. This is not the case with points valuated by formulas: if you select an axis system, the defined formula remains unchanged.
Important: If you create a point using the coordinates method and an axis system is already defined and set as current, the point's coordinates are defined according to current the axis system. Warning: The current local axis system must be different from the absolute axis. Click Compass Location tab.
If the compass is lying on the geometry, the X, Y, and Z coordinates of the point are modified according to the location of the compass. However, if the compass is not lying on the geometry, i.e. it is at default location, clicking this button would display an error message, and the point would be created using existing specified coordinates.
Important: The Compass Location tab is disabled when any of the X, Y, or Z coordinate is specified using a formula. Click OK to create the point.
The point (identified as Point.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
![]()
Create a Point on a Curve
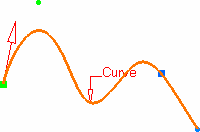
You can create a point on a curve at a distance from a reference point.
Click Point
 .
.The Point Definition dialog box appears.
In the Point type list, select the On curve point type.
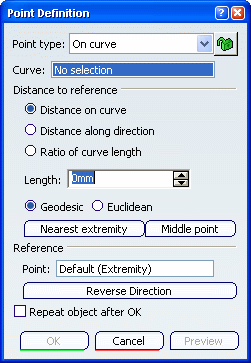
Optional: In the Curve box, select a curve.
In the Point box, select a reference point.
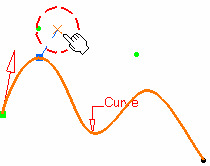
If this point is not on the curve, the minimum distance between the point and the curve is computed. If no point is selected, the curve's extremity is used as reference.Select an option point to determine where the new point is to be created:
- Distance on curve: it is created at a given distance along the curve from the reference point. A distance value needs to be specified.
- Distance along direction: it is created along a specified direction and at an offset distance from the reference point. Direction and offset values need to be specified.
- Ratio of curve length: it is created at a given ratio between the reference point and the curve's extremity. A ratio value needs to be specified.
Select where distance is to be measured:
- Geodesic: the distance is measured along the curve.
- Euclidean: the distance is measured in relation to
the reference point (absolute value). Therefore, Distance on
curve and Ratio of curve length are
unavailable.
The corresponding point is displayed.
Warning: - It is not possible to create a point with an Euclidean distance if the distance or the ratio value is defined outside the curve.
- These options are unavailable with the Distance along direction option.
You can select either Nearest extremity to display the point at the nearest extremity of the curve or Middle point to display the mid-point of the curve.
Warning: - Be careful that the arrow is orientated towards the inside of the curve (providing the curve is not closed) when using the Middle point option.
- These options are unavailable with the Distance along direction option.
Click Reverse Direction to display either the point on the other side of the reference point (if a point was selected originally) or the point from the other extremity (if no point was selected originally).
Select the Repeat object after OK check box to create equidistant points on the curve, using the currently created point as the reference.
Refer to Creating Multiple Points and Planes.
Warning: This option is unavailable with the Distance along direction option. Click OK to create the point.
The point (identified as Point.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Important: - If the curve is infinite and no reference point is explicitly given, by default, the reference point is the projection of the model's origin
- If the curve is a closed curve, either the system detects a
vertex on the curve that can be used as a reference point, or it
creates an extremum point, and highlights it (you can then select
another one if you want) or the system prompts you to manually
select a reference point. Extremum points created on a closed curve are aggregated under
their parent command and put in no show in the specification tree.

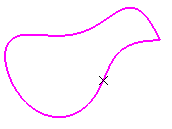
- If the input point is selected automatically and you change the type, it is not retained to the new type. For instance, an extremum feature would not be retained if you change its type from On curve to Coordinates.
- If the input for the curve is a feature, and an extremum point exits on this curve, the point is used as reference point. If the input for the curve is a part of a geometric feature (here an edge), and even though an extremum point already exists on this geometric feature, a new extremum is created.
![]()
Create a Point on a Plane
You can create a point on a plane at a distance from a reference point.
Click Point
 .
.The Point Definition dialog box appears.
In the Point type list, select the On plane point type.
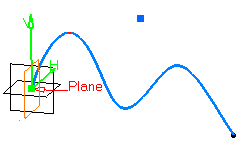
In the Plane box, select a plane.
If you select one of the planes of any local axis system as the plane, the origin of this axis system is set as the reference point and featurized. If you modify the origin of the axis system, the reference point is modified accordingly.
Optional: Select a point to define a reference for computing coordinates in the plane.
If no point is selected, the projection of the model's origin on the plane is taken as reference.
Optional: Select a surface on which the point is projected normally to the plane.
H and V are computed from the directions belonging to the geometrical plane.
If the plane is moved, during an update for example, the reference direction would then be projected on the plane.
Click in the plane to display a point.
Click OK to create the point.
The point (identified as Point.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
![]()
Create a Point on a Surface
You can create a point on a surface at a specified distance and direction from a reference point.
Click Point
 .
.The Point Definition dialog box appears.
In the Point type list, select the On surface point type.
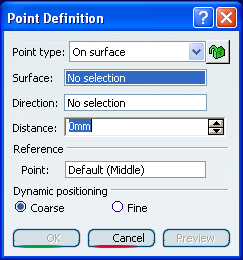
In the Surface box, select the surface where the point is to be created.
Optional: Select a reference point. By default, the surface's middle point is taken as reference.
Optional: Select an element to take its orientation as reference direction or a plane to take its normal as reference direction. You can also use the contextual menu to specify the X, Y, Z components of the reference direction.
Enter a distance along the reference direction to display a point.
Choose the dynamic positioning of the point:
- Coarse (default behavior): the distance computed
between the reference point and the mouse click is an Euclidean
distance. Therefore, the created point may not be located at the
location of the mouse click (see picture below).
The manipulator (symbolized by a red cross) is continually updated
as you move the pointer over the surface.
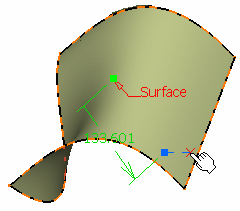
- Fine: the distance computed between the reference
point and the mouse click is a geodesic distance. Therefore the
created point is located precisely at the location of the mouse
click.
The manipulator is not updated as you move the pointer over the
surface, only when you click on the surface.
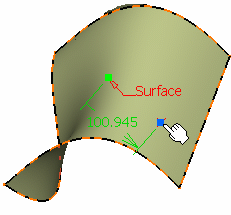
- Coarse (default behavior): the distance computed
between the reference point and the mouse click is an Euclidean
distance. Therefore, the created point may not be located at the
location of the mouse click (see picture below).
The manipulator (symbolized by a red cross) is continually updated
as you move the pointer over the surface.
Click OK to create the point.
The point (identified as Point.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Note:
- The dynamic positioning option is persistent but is not stored in the feature. Therefore at edition, the dynamic positioning may not be the one you selected.
- Sometimes, the geodesic distance computation fails. In this case, an Euclidean distance might be used and the created point might not be located at the location of the mouse click. This is the case with closed surfaces or surfaces with holes. We advise you to split these surfaces before creating the point.
![]()
Create a Point Using the Center of a Circle/Sphere/Ellipse
You can create a point at the center of circle, sphere or ellipse.
Click Point
 .
.The Point Definition dialog box appears.
In the Point type list, select the Circle/Sphere/Ellipse point type.
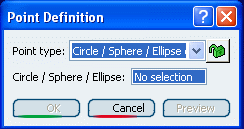
Select either a circle, circular arc, ellipse, sphere or portion of sphere.
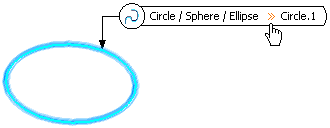
A point is displayed at the center of the selected element.
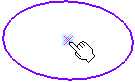
Click OK to create the point.
The point (identified as Point.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
![]()
Create a Point Tangent on a Curve
You can create a point tangent to the curve by selecting a curve and tangent direction.
Click Point
 .
.The Point Definition dialog box appears.
In the Point type list, select the Tangent on curve point type.
Select a planar curve and a direction line.
The Multi-Result Management dialog box is displayed because several points are generated.
Refer to Managing Multi-Result Operations.
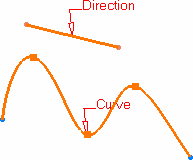
Click OK to create the point.
The point (identified as Point.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
![]()
Create a Point Between Two Points
You can create a point between two existing points using a ratio value.
Click Point
 .
.The Point Definition dialog box appears.
In the Point type list, select the Between point type.
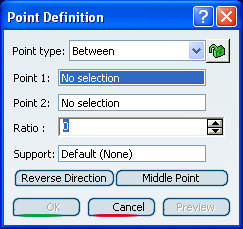
Select any two points.
Enter the ratio, that is the percentage of the distance from the first selected point, at which the new point is to be.
You can also click Middle Point to create a point at the exact midpoint (ratio = 0.5).
Important: Be careful that the arrow is orientated towards the inside of the curve (providing the curve is not closed) when using the Middle Point option. If the curve is closed, the point is created along the orientation of the curve. Optional: Select a Support. It can be a surface or a curve.
If a support is selected, the point is created between the two points measured along the support. If the support is a curve, the distance along the curve is used. If the support is a surface, the created point lies on the computed geodesic curve between the two points on the surface.
Important: - If the ratio is less than 0 or greater than 1, the point is created along the extrapolated curve tangent to the support. In this case, the created point may not lie on the support. For a closed curve, the point is created along the orientation of curve. If you want to create the point along another part of the closed curve, the input points should be selected in reverse order.
Warning: - Points must lie on the support, otherwise an error message is issued.
- In some cases, it may not be possible to create a point on a surface with a hole or a closed surface (for instance, if the geodesic curve encounters a hole).
Click Reverse direction to measure the ratio from the second selected point.
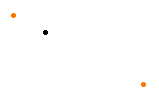
If the ratio value is greater than 1, the point is located on the virtual line beyond the selected points.
Click OK to create the point.
The point (identified as Point.xxx) is added to the specification tree.