More about Chamfers | ||||
|
| |||
Extremities
Four extremities types are available:
- Smooth: a tangency constraint is imposed at the connection between the chamfer and the support surface, thus smoothing the connection
- Straight: no tangency constraint is imposed at the connecting point between the chamfer and the initial support, generating sometimes a sharp angle
- Maximum: the chamfer is limited by the longest selected edge
- Minimum: the chamfer is limited by the shortest selected edge
![]()
Propagation
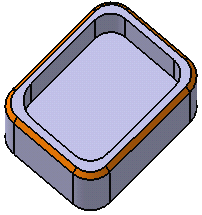
Two propagation modes are available:
- Minimal: Edges tangent to selected edges can be taken into account to some
extent. The application continues chamfering beyond the selected
edge whenever it cannot do otherwise. In our example below, the
chamfer is computed on the selected edge and on a portion of
tangent edges:
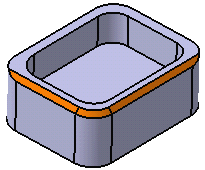
- Tangency: Chamfers the entire selected edge as well as its tangent edges.
It continues chamfering beyond the selected edge until it
encounters an edge that is non-continuous in tangency as shown in
our example: