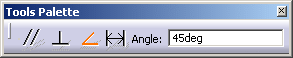
- Directional constraint: A directional constraint is the one which constrains the direction of the profile segment. This can be achieved either through the parallel, perpendicular or angle constraint functionality.
When such a constraint is applied, the position of the profile segment is defined by the starting point of the selected profile segment, but the directional constraint is applied according to the selected directional constraint.
- Parallel: The section profile is created parallel to the selected reference element and passing through the first point. This constraint is active by default.
- Perpendicular: The section profile is created perpendicular to the selected reference element and passing through the first point.
- Angle: The section profile is created at the specified angle, in a counter-clockwise direction relatively to the selected line. When selecting this constraint, the Angle: field appears, allowing you to enter the desired angle.
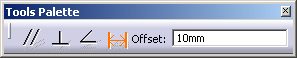
- Positional constraint: A positional constraint is the one which constrains the position of the profile segment, along with the direction. This is achieved through the offset constraint functionality. When an offset constraint is applied, the starting point of the profile segment is recomputed in order to fix the position of the profile segment at the specified distance from the reference element.
- Offset: The section profile is created with the specified offset, parallel to the selected reference element (on the same side as the reference element in the case of a positive value, on the opposite side in the case of a negative value). When selecting this constraint, the Offset: field appears, allowing you to enter the desired offset value.
|

