Click
Isophotes Mapping Analysis
The
Isophote Analysis dialog box is displayed.
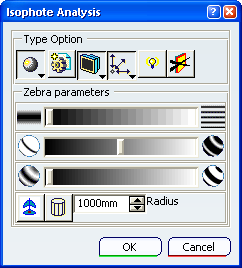
In the Type Option area of the dialog box select
Cylindric Mode .
.
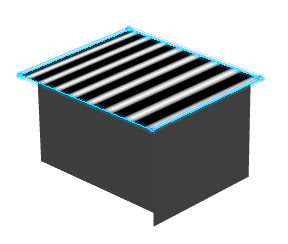
Click a surface in the 3D area.
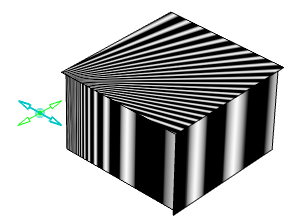
Isophotes representing cylindrical zebra stripes are applied on
the surface.
In the Type Option area select
Analysis mapping on part .
.
Isophotes are displayed on all surfaces of the part, irrespective of whether they are selected or not.
Note:
If you want isophotes on all of the part in the 3D area, use this method of global selection rather than using a trap.
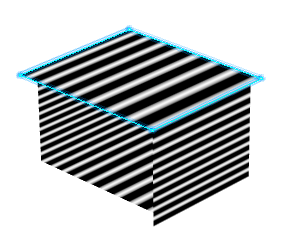
In the Type Option area of the dialog box select
Spheric Mode .
.
Isophotes representing spherical zebra stripes are applied on
the surface.
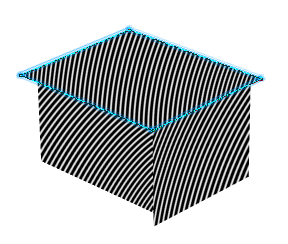
In the Zebra parameters area select
Compass .
.
The compass is repositioned at the center of the reference planes and a representation of the spherical 3D manipulator is displayed with its center located at the base of the compass.
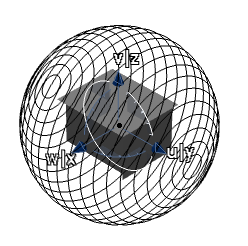
In the Type Option area of the dialog box select
Cylindric Mode .
.
The 3D manipulator changes to a cylindrical shape.
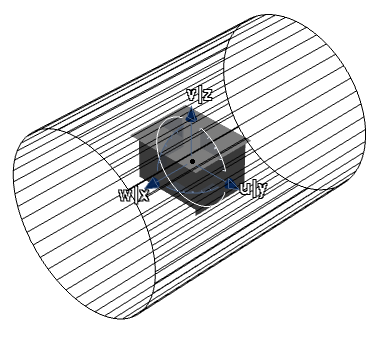
In the Zebra parameters area select
Hide the 3D manipulator .
.
The 3D manipulator disappears, but the compass remains in the 3D area.
Manipulate the compass to modify the orientation of the hidden 3D manipulator.
Because the 3D manipulator orientation has changed, the orientation of the isophotes also changes.
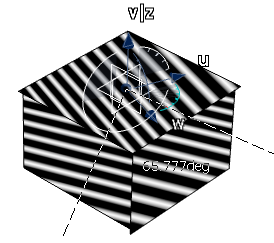
In the Type Option area select
User eye .
.
Note that Point Mode is selected automatically.
is selected automatically.
Note:
If you right-click the
Eye user manipulator a contextual menu appears which allows you to Edit its position or Keep this point.
When you have finished working with this command, do one of the following:
- To create the analysis, click OK.
The analysis is added to the specification tree where it is identified as Command_Name.Analysis.x.
The analysis will be updated automatically whenever you modify any of the elements in the analysis (for example when you deform an element using control points).
- To abandon the analysis, click Cancel.