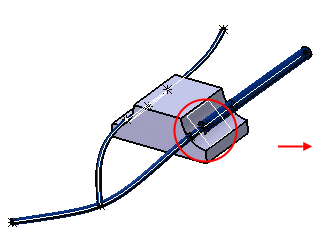
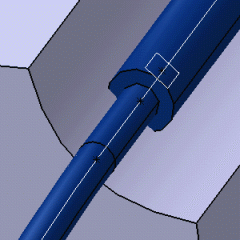
More about Routing along Retainers | ||||
|
| |||
Routing along Retainers
When you route a branch along a retainer, the branch curve is built as follows:
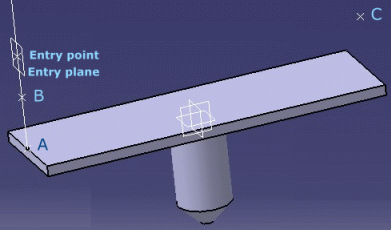
- The entry point is published as RefPoint1.
- It is projected onto the base plane (RefBasePlane) as A.
- A line is created between A and the entry point (RefPoint1).
- A point (B) is created on this line, knowing that the distance between A and B is equal to the branch radius.
- The point B is projected onto RefPlane2 as C.
- The points B and C are added to the branch center curve definition. Any slack between these points is ignored.
All construction objects are placed in the No Show space.
length = branch diameter * 0.5
When the diameter changes, the branch is re-computed using this formula to keep it in contact with the retainer base plane.
Concerning flat cables, the cable is parallel to the base plane and it is moved so that it can be stuck on the base plane.
length = flat cable thickness * 0.5
| Warning:
If you add a branch point splitting the branch into two segments in
the middle of the retainer, only one segment will be re-computed to
keep it in contact with the retainer base plane.
|