About the Multi-View Mode | ||
| ||
Basic Vocabulary
To take full advantage of the three scenarios provided, you need to be familiar with the basic vocabulary.
- "Viewer" is the screen area in which 3D objects are drawn
- "View" is a part of the viewer. Usually, the viewer has one single view but it can also be divided into 4 parts representing a different view each. When a viewer is split into several views, it is identified as a "multi-view" viewer
- "Viewpoint" is the set of parameters required for defining a 3D view volume, i.e. the eye of the user, the view direction, the focus point and the axis system defining the position of the user. It can be defined as the position in model coordinates at which the eye is looking
- "Layout" defines how the viewer is divided into different areas (= views) and how these areas are located
- "Configuration" is a layout made up of views, each of them being defined with a viewpoint.
![]()
How Configurations are Applied?
The multi-view configuration remains active throughout the whole V6 session but it is not saved when selecting .
For instance, if you apply a multi-view configuration then save and close your object before reopening it, the object is displayed in a single-view configuration using the last active view before the save.
Only the last configuration is stored in the CATSettings directory and
you can reuse it from one session to another by clicking Create Multi-View
![]() in the View toolbar. If no customization has been defined, the
default configuration is applied. Remaining individual configuration settings are not stored in
the CATSettings directory. Therefore:
in the View toolbar. If no customization has been defined, the
default configuration is applied. Remaining individual configuration settings are not stored in
the CATSettings directory. Therefore:
- When you select for the first time in a session, the Views & Layout dialog box displays the last configuration applied in a previous session (default values are applied to the other configurations). If no multi-view configuration has been applied in a previous session, default values are applied to all configurations.
- When you reselect in the same session, the last used tab is activated with the last applied configuration.
![]()
Manual Tab
In a manual configuration, you can select the configuration to be applied to view your objects from a list of predefined configurations.
This tab is made up of five areas:
- Configuration Selection lets you select a predefined multi-view configuration from the list.
- View Selection lets you set the current view as well as the orientation of the selected viewpoint.
- Viewpoint Manipulation lets you manipulate the viewpoint
using the following options:
- Rotation Lock: locks the viewpoint rotation.
- Translation Lock: locks the viewpoint translation.
- Viewpoint Synchronization: imposes a synchronization between the views when a viewpoint transformation (rotation, translation or zoom) is made in one of them. Note that you cannot activate both Translation Lock and Viewpoint Synchronization.
- Standard Views icons let you set the desired standard view as the current view. The standard views displayed in the left part of the dialog box are identical to the one of the Quick View toolbar.
- Confirmation: lets you validate or cancel the configuration.
The Configuration Selection area lets you choose among several configurations.
Four-View
The viewer is divided into four equal views, each of them being identified as follows:
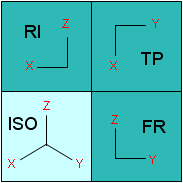 |
RI = Right View TP = Top View FR = Front View ISO = Isometric View |
Main view to the right
The viewer is divided into two parts. The main view is displayed to the right and three auxiliary views are displayed to the left:
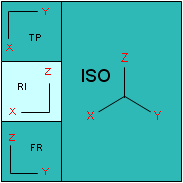 |
RI = Right View TP = Top View FR = Front View ISO = Isometric View |
Main view on top
The viewer is divided into two parts. The main view is displayed on top and three auxiliary views are displayed at the bottom:
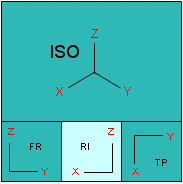 |
RI = Right View TP = Top View FR = Front View ISO = Isometric View |
![]()
Automatic Tab
In an automatic configuration, you can select the standard view to be set as the base view around which adjacent views are automatically generated.
This tab is made up of three areas:
- View Selection lets you select a group of views as well as their location and orientation.
- Viewpoint Manipulation lets you manipulate the viewpoint
using the following options:
- Rotation Lock: locks the viewpoint rotation.
- Translation Lock: locks the viewpoint translation.
- Viewpoint Synchronization: imposes a synchronization between the views when a viewpoint transformation (rotation, translation or zoom) is made in one of them. Note that you cannot activate both Translation Lock and Viewpoint Synchronization.
- Confirmation: lets you validate or cancel the configuration.
For any 3D object, there are six standard views according to the coordinate system of the object. These views are mapped onto a cube, each face of this cube being perpendicular to one of the directions of the 3D axis. Whatever the orientation of the cube, the observer can see three faces (i.e. three standard views) as shown below:
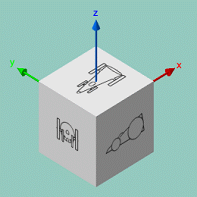
An isometric view can be added to these views. The direction of this isometric view starts from the vertex formed by the three faces towards the center of the cube.
The View Selection area represents the unfolded cube of standard views: each square represents a standard view and the one placed at the center is the base view around which adjacent views are automatically generated. In the default configuration displayed below, the base view is the standard Left View:
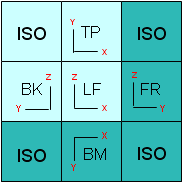 |
ISO = Isometric View TP = Top View BK = Back View LF = Left View FR = Front View BM = Bottom View |
![]()
Standard Views Tab
You can customize the direction of standard views along the X, Y and Z axes within a 3D viewer.
This tab is made up of six areas:
- Standard views icons let you select the standard view to be customized.
- View Selection lets you modify the direction and orientation of the selected standard view.
- View Direction lets you manipulate the viewpoint.
- Apply to axis lets you specify the axis to which the modification will be applied.
- Reset All lets you restore all the standard views to their original default direction and orientation.
- Confirmation: lets you validate or cancel the configuration.