|
This article presents the Logical modeler, and explains how
to customize it.
|
Description
This section first presents the objects representing the Logical
modeler. Then it describes how this object model view has been translated towards
PLM objects based on PLM Core Modeler objects. You will see the description of each
PLM package defining these PLM objects.
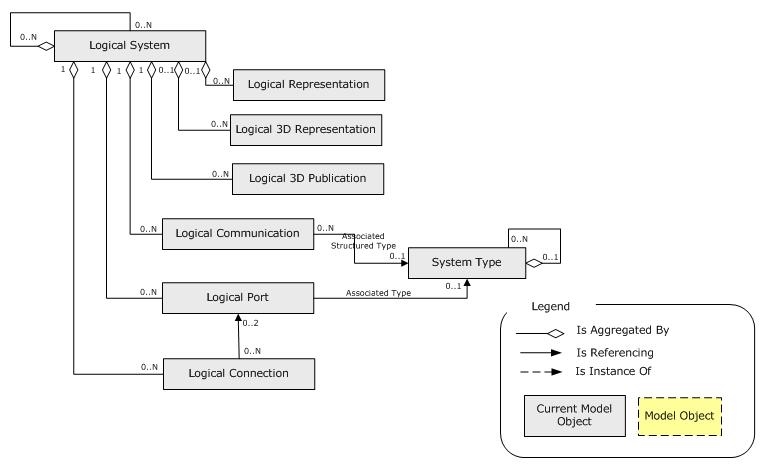
Conceptual Model
The Requirement (R), Functional (F), Logical (L) and Physical
(P) domains allow the whole definition of a product. In other words, it is used
for the Product Conception Approach (Product Concept Creation) based on the
description of the product through different levels of abstraction (RFLP).
Within RFLP domains, the Logical domain enables to define
HOW to engineer the product to satisfy the functional systems (i.e. services)
specified in Functional domain. Logical systems and links between logical systems
through their ports specify the network.
This is summarized in the following UML schema:
Implementation Model
The Logical model is implemented with PLM Core Object as follows:
Fig.2 PLM Core Objects
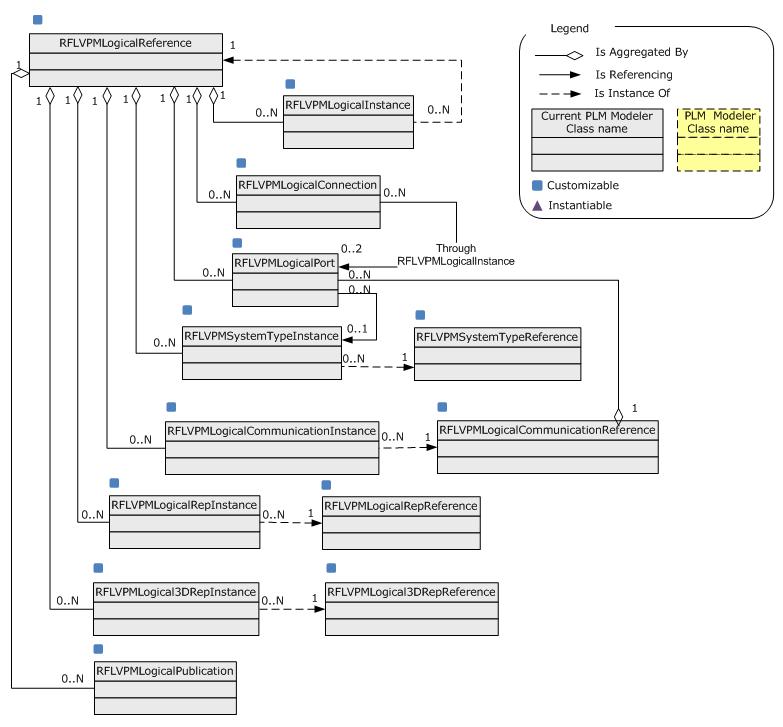 |
The following array shows the links between the conceptual and PLM Core objects:
Business Logic
This section lists and describes the PLM Opening ID implemented by the following
PLM classes of the Logical modeler.
RFLVPMLogicalReference , Implemented Business
Logic
RFLVPMLogicalInstance , Implemented Business
Logic
RFLVPMLogicalRepReference , Implemented Business
Logic
RFLVPMLogicalRepInstance , Implemented Business
Logic
RFLVPMLogicalPort , Implemented Business Logic
RFLVPMLogicalConnection , Implemented Business
Logic
RFLVPMSystemTypeReference , Implemented Business
Logic
RFLVPMSystemTypeInstance , Implemented Business
Logic
RFLVPMLogicalCommunicationReference , Implemented
Business Logic
RFLVPMLogicalCommunicationInstance , Implemented
Business Logic
RFLVPMLogical3DRepReference , Implemented
Business Logic
RFLVPMLogical3DRepInstance , Implemented Business
Logic
RFLVPMLogicalPublication , Implemented Business
Logic
Customization
Customization first deals with the modeler PLM package customization [2].
It consists in to create a new package containing new PLM classes for each
"Customizable" PLM class of the modeler PLM package. Then, you should
take into account the UI masks creation to create either a new security mask file,
or to update the default one [3]. Finally, you can integrate
your own business logic on each new PLM classes by implementing provided PLM opening
ID [4].
PLM Package Customization
This part consist in to create a new package when the modeler PLM package must
be customized.
Must be fully customized.
Must be fully customized.
Must be fully customized.
Must be fully customized.
Must be fully customized.
UI Mask Customization
When a PLM attribute is defined (inside modeler PLM package) some features like
its editability criteria, mandatory /optional option, can be overwritten by UI
mask. You can say this PLM attribute is not writable in Query context, this PLM
attribute is mandatory in Create context, this user PLM attribute is not never visible
and so one. A set of UI masks form a security mask file. We say security mask because
it is associated with these files security information. For a people, and a given
context can be associated a security mask.
For each customized Modeler PLM package, at least one UI mask file must be created
(for the default security mask ), since it must contain the new PLM Attributes.
When you use the tool to create a customization, a default UI mask file is provided
taken into account the added PLM attributes. You can modify the default file to
introduce your change.
Rules to respect for a new UI mask creation
No specific rule to customize UI mask file.
Business Logic Customization
You can yourself integrate your business logic for each customization of:
- RFLVPMLogicalRepReference
- RFLVPMSystemTypeReference
- RFLVPMLogicalCommunicationReference
- RFLVPMLogicalCommunicationInstance
- RFLVPMLogical3DRepReference
- RFLVPMLogical3DRepInstance
References
History
| Version: 1 [Oct 2008] |
Document created |