Running the Fastening Rules Analysis | ||||
|
| |||
Click Fasteners Check
 in the Fastener Review toolbar.
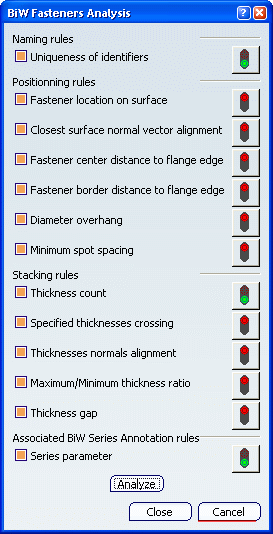
in the Fastener Review toolbar.The BiW Fasteners Analysis dialog box opens.

Check the rules on which you want to run the analysis.
- Naming rules enable to check that the fasteners have been correctly
named.
- Uniqueness of identifiers: checks that all fasteners have different names
- Positioning rules enable to check the position of fasteners.
- Fastener location on surface: checks that spots are located on surfaces.
- Closest surface normal vector alignment: checks that the fastener's normal vector is parallel to the computed normal at the projection point on the closest surface.
- Fastener center distance to flange edge: checks that all fasteners on crossed surfaces intersect all specified components and computes the minimum distance from the fastener's center location to the closest flange edge.
- Fastener border distance to flange edge: checks that all fasteners on crossed surfaces intersect all specified components and computes the minimum distance from the fastener's border location to the closest flange edge.
- Diameter overhang: checks the maximum overhang of the fastener diameter to the closest flange edge. Note that internal edges and tangent surfaces are ignored, but holes are not. For rivets, the diameter taken into account is the shaft diameter.
- Minimum spot spacing: checks that the minimum spot spacing between two spots is compliant with the value set in the BiW parameters.
- Stacking Rules enable to check the fastener location with respect to the
stacking order.
- Thickness count: checks that the number of thicknesses is compliant with the number set in the BiW parameters.
- Specified thicknesses crossing: checks that spots cross all the specified thicknesses of the fastener set.
- Thicknesses normals alignment: checks that the thickness normal to the crossed joined components is aligned with the fastener normal.
- Maximum/Minimum thickness ratio: checks that the
ratio between the minimum and the maximum thicknesses of the
crossed zones is lower or equal to the maximum defined ratio, even
if all fasteners do not intersect all the specified joined
components.
Important: - In case the maximum ratio is set to 1, the rule checks that all crossed thicknesses are equal.
- If one or more thicknesses are null, the ratio is infinite.
- Thickness gap: checks that the gap
value between two joined components crossed by a given fastener is compliant with the value set in the BiW parameters.
Important: - The above three rules apply for spot points and spot projection welds only, not curve beads.
- In case two or more surfaces with common edges are crossed, you need to perform a join operation so that their free edges are considered as those of one single surface.
- Associated BiW Series Annotation rules enable to check parameters attached to annotations.
- Series parameter: checks that all parameters attached to the annotation (for instance, the number of fasteners or fastener set reference name) are compliant with the parameters associated to the reference Fastener type (for instance, Resistance Spot Welding)
- Naming rules enable to check that the fasteners have been correctly
named.
Click Analyze.
Besides each rule, a sign gives a feedback whether the check passed or failed.
All failing elements are selected and highlighted in the 3D geometry for a further check that will take into account only the current selection.
Click the red sign corresponding to the rule that failed.
The corresponding check failure analysis window opens, along with the list of selected failing elements. You can select several elements in the list to highlight them in the specification tree and 3D geometry.
Here is an example with the Location on surface check failure dialog box report:
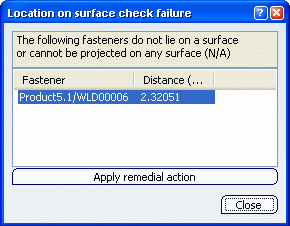
- The Fastener location on surface check failure report displays either "N/A" if the fastener cannot be projected on any surface or the distance to the closest surface. Click Apply Remedial action to heal the fasteners in error and project them onto the closest surface.
- The Closest surface normal vector alignment check failure report displays either "N/A" when no normal vector is found on the fastener or the deviation angle between the normal vector of the fastener and the normal vector at the projection on the closest surface. Click Apply Remedial action to heal the fasteners in error and reset the normal vector according to the normal vector at the projection on the closest surface.
-
The Fastener center distance to flange edge,
Fastener border
distance to flange edge, or Diameter overhang ratio check failure
report displays either "N/A" when no free edge can be found on
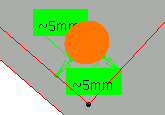
any crossed surface or the distance of the failed fasteners. It highlights the closest edges involving the failure in the 3D
geometry, for instance when a fastener is equidistant between
several edges (see picture below).
Tips:
|