IGES | ||
| ||
![]()
Import
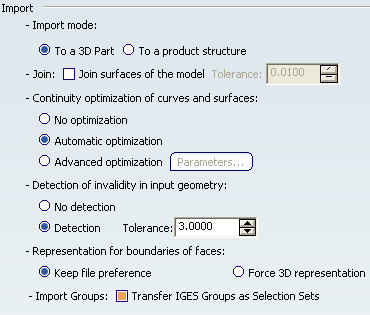
Select the desired option:
- Import mode
-
When To a 3D Part is selected, an IGES file is imported to a 3D Part, that is a Product with an aggregated representation:

Note: the invisibility status of 408 entities is not taken into account.
For large files containing a large number of 308/408 IGES entities, you can select the option To a product structure . The IGES file
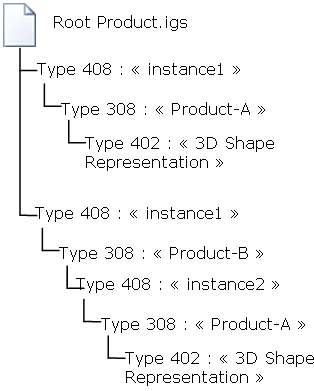
is imported to a structure like this one: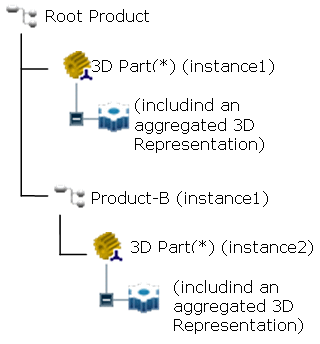
Note: the invisibility status of 408 entities is taken into account.
The uniqueness of the component name is ensured by adding a suffix corresponding to the DE (Directory Entry) number of the IGES 308 entity (subfigure definition).
Note:
- Even if the IGES file contains only geometry, the result of the import is a 3D Part.
- If a representation is instantiated several times in the IGES file, its geometry is duplicated and placed in 3D Parts.
 By default,
Import mode is set to To 3D Part.
By default,
Import mode is set to To 3D Part.
- Join
-
Select the option Join surfaces of the model to join the surfaces of your IGES model into a shell: the software will try to knit the surfaces from an importable file into a shell, even if the file contains Groups (402).
Once this option is selected, you can edit the Tolerance which is used to join the surfaces of the model: If you know the tolerance of the system which has created the IGES file, you can use it. Otherwise, it is better to begin with a small tolerance.
Note:
- If you select this option to import IGES files, make sure that the model is constituted of one part.
- The Join operation may fail in specific topological configurations.
- This option does not apply to Manifold Solid Brep (IGES type 186): the faces are always imported into a join.
- When the Import as a Product Structure option is active, the option Join surface of the model is selectable but has no effect.
 By default,
Join surfaces of the model is not selected.
By default,
Join surfaces of the model is not selected.
- Continuity optimization of curves and surfaces
-
This setting allows a better user control over the number of curves and surfaces that are created during the process of importing STEP data into V6:
- V6 requires its geometry to be C2-continuous. When non C2-continuous geometry must be imported from a IGES file, this geometry (curves, surfaces) is broken down into a set of contiguous geometries, each of them being C2-continuous. This is what happens when the No Optimization option is chosen.
- However, this can produce an increase of the size of the resulting data, because more curves/surfaces are created. In order to limit this drawback, two other modes are optionally offered.
- In those modes, the IGES interface tries to limit the splitting of curves and surfaces by modifying their shape slightly, so that they become C2-continuous while remaining very close to their original shape.
- In order to guarantee that the deformation is not excessive, a maximum deviation (tolerance) parameter is used. When in Automatic optimization mode, the value read from the IGES file is corrected so that it remains lower than 0.001 mm. This guarantees an optimization that remains compatible with the precision for the data that was set by the emitting system.
- Last, if this strategy is not enough, you can choose the Advanced optimization mode, in which an arbitrary deviation value can be entered.
 By default,
the Automatic Optimization is
proposed:
By default,
the Automatic Optimization is
proposed:- No approximation , thus this option does not create a significant deformation and keeps the internal BSpline structure (equations and knots.
- A continuity optimization is performed within the default value
for deformation tolerance (0.001 mm) on:
- BSpline surfaces,
- all types of curves with the exception of canonical curves (3D and P-curves when available),
Note:
- The parameters box cannot be activated
- This option soften the effect C2 cutting of faces and boundaries (which is mandatory in V6) without any significant geometric deformation.
If you select No optimization:
- No optimization is performed on BSplines (neither curves nor surfaces).
- Elements are cut at discontinuity points to suit the modeler (exact mathematic continuity). This may result in a dramatic number of faces and boundary curves, data of poor quality and poor performances in further use in V6.
If you select Advanced Optimization:
- No approximation. The internal BSpline structure (equations and knots) is kept,
- A continuity optimization is performed on:
- BSpline surfaces,
- all types of curves (3D and P-curves when available),
but the deformation tolerance is set by the user (see Parameters).
With this option, you can enter a larger tolerance value which may enhance the optimization impact (resulting in less C2 cutting on faces).
 By default,
Automatic Optimization is selected.
By default,
Automatic Optimization is selected.
- Parameters
- When Advanced optimization is selected, Parameters gives access to advanced optimization options and tolerances.
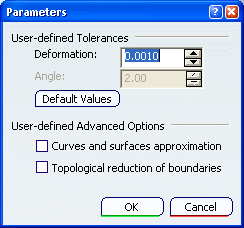
Deformation : maximum deformation (in millimeter) allowed in the optimization of curves and surfaces. Ranges between 0.0005 and 0.1 mm.Important: the tolerance is shared by the optimization process (in all cases), the Curves and surfaces approximation and the Topological reduction of boundaries if you have selected those check boxes. For example, the deformation tolerance is 0.001mm and Curves and surfaces approximation is selected. The tolerance for the optimization will be 50%, i.e. 0.0005mm and that of the Curves and surfaces approximation will also be 50%. Thus, the number of cuts of the faces will vary according to the value entered, and according to the number of check boxes selected.
Angle : angle (in degree) below which contiguous elements can be merged. Ranges between 0 and 10 degrees. By default,
Deformation is set to 0.001.
By default,
Deformation is set to 0.001. By default,
Angle is set to 2.
By default,
Angle is set to 2.Default Value reverts to the default values.
Curves and surfaces approximation alone:
- BSpline surfaces and curves continuity is optimized.
- In addition, Bspline curves and surfaces approximation is performed.
- It is possible to enter a user value for Deformation.
- This option usually results in a significant decrease in the number of faces cuttings.
Topological Reduction of Boundaries alone:
- BSpline surfaces and curves continuity is optimized,
- In addition, topological reduction is applied to boundaries,
- The Angle value is used to select contiguous curves that can be merged into a smooth one (tangency criteria),
- It is possible to edit the values for Deformation and Angle,
- This combination of options usually results in a significant decrease in the number of boundary curves (especially on poor quality input data.
Curves and Surfaces Approximation and Topological Reduction of Boundaries together:
- BSpline surfaces and curves continuity is optimized
- In addition, BSpline curves and surfaces approximation is performed and topological reduction is applied to boundaries
- It is possible to enter user values for Deformation Tolerance and tangency Angle.
- This combination of options allows the utmost optimization of curves and surfaces, while keeping geometric deformation under control. It results in reducing the number of faces and boundaries and ensures better performance in downstream use of the data.
You can find useful information in the report file. Please see the Report file section in the IGES Import chapter in this User's Guide.
 By default,
Curves and Surfaces Approximation and
Topological Reduction of Boundaries are not selected.
By default,
Curves and Surfaces Approximation and
Topological Reduction of Boundaries are not selected. - Detection of invalidity in input geometry
-
You can choose to import IGES files with or without detecting discrepancies in geometry, by selecting the corresponding option.
The detection of invalidities applies only to 3D curves of boundaries for IGES faces of type 143 and 144. The invalidities found are:
- hole in a boundary. A 3D annotation Single boundary with hole size: value mm is attached to the discrepancy found.
- boundary too far apart from the surface. A 3D annotation3D curves do not map with the surface is attached to the discrepancy found.
The 3D annotations are placed in an AnnotationSet in the specification tree.
Detection enables you to enter the Tolerance value above which a geometry is considered as invalid. It corresponds to:
- the size of a hole in an open boundary,
- the distance between the boundary loop and the surface.
 By default,
Detection is selected and Tolerance is set to 3 mm.
By default,
Detection is selected and Tolerance is set to 3 mm.
- Representation for boundaries of faces
-
There are two type of IGES faces:
- Trimmed Parametric Surfaces (IGES entity type 144)
- Bounded Surfaces (IGES entity type 143).
They are defined by:
- a support surface (ex. IGES entity types 120: Surfaces of Revolution or 122: Tabulated Cylinders or 128: BSpline Surfaces)
- one or more boundaries (IGES entity types 142 and 141, resp.)
The boundaries of those faces (respectively type 142 and 141) have two representations:
- 2D or P-Curves (parametric)
- 3D (spatial).
For each boundary, the IGES file contains a parameter defining the preferred representation:
- 3D,
- 2D,
- none,
- equal preference.
In the three last cases, V6 tries to import the 2D representation of the boundary. In case of failure, the 3D representation is imported. If the preferred representation is 3D, but if there is a failure, then the 2D representation will be imported.
3D curves can be used with every type of surfaces and curves whereas 2D curves can be used:
- when the surface is
- B-Spline (type 128),
- non-closed C2 Ruled surface (type 118),
- Surface of revolution (type 120) or
- Tabulated cylinder (type 122)
- and if these curves are P-Lines (type 110, form 0) or P-Nu(r)bs (type 126).
Using 2D or P-Curves instead of 3D Curves as face boundaries allow better performances (it is not necessary to lay down or project 3D Curves on the surfaces) and quality improvements (faces that could be KO because of invalid, unsupported or missing 3D Curves will be processed with P-Curves and correctly transferred).
When the Keep File Preference option is active, the curves representation which is taken into account is:
- 2D if the IGES file preference (5th parameter of the entity
type 142) is:
- 0 (unspecified),
- 1 (2D representation is preferred) or
- 3 (2D and 3D are equally preferred),
- 3D if the IGES file preference (5th parameter of the entity type 142) is 2 (3D representation is preferred)
- or if the input geometrical elements do not allow to use 2D curves (see above).
If you do not wish to use the 2D representation (i.e. if you want to override the preference set in the IGES file), select the Force 3D representation option. Only the 3D representation will be imported.
Important: - 2D or P-Curves are not used if either the IGES file indicates the preference is 3D Curves or Force 3D Representation is selected. In such cases, 3D curves are used.
- 2D or P-curves will be used in a second try to create the face if all the conditions below are fulfilled:
- the file preference is 3D Curves,
- the import to V6 of the face fails (using the 3D curves), -
- Force 3D Representation is not selected,
- the file contains 2D curves that can be used for import to V6,
- Any problem with the boundary components and/or processing is written in the .err file.
- 2D or P-curves are not used with any surface type other than the ones described above (type 114, 108, 190, 192, 194, 198,...)
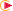 By default,
Keep file preference is selected.
By default,
Keep file preference is selected. - Import Groups
-
Transfer IGES Groups as Selection Sets imports IGES groups (Entity Type 402, Forms 1-7-14-15: Associativity Instance) as Selection Sets.
You can de-select this option for a faster import.
Note: Selection Sets will not be created.
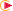 By default,
Transfer IGES Groups as Selection Sets is selected.
By default,
Transfer IGES Groups as Selection Sets is selected.
![]()
Export
Select the desired option:
- Export only shown entities
-
When the Export only shown entities option is not selected, all entities are exported, even if they are not visible. They will be identified (Status Number) as invisible in the IGES file.
Regarding occurrences in a product structure:
- when the visibility status is not the same for two different instances of a reference, the BOM is respected and kept.
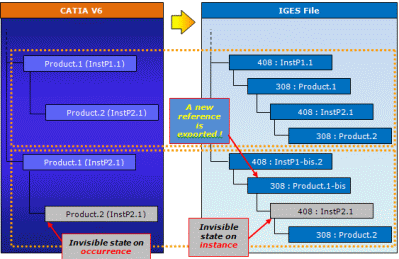
- when the visible status is not the same on two occurrences of the same instance of a reference, the output is wysiwyg, but the BOM is not respected as a new reference is created:
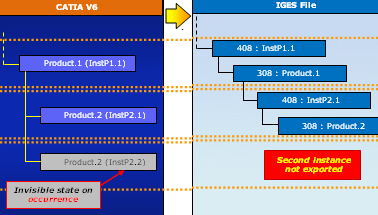
When the Export only shown entities option is selected, it allows you to save only the entities which are in the Show mode.
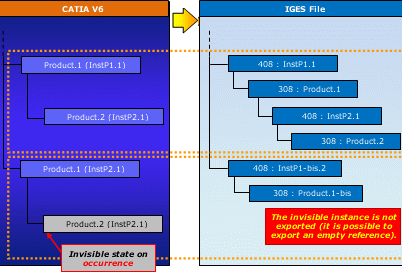
- When the visibility status is not the same on two different instances of a reference, this is what is exported:
- When the visibility status is not the same on two occurrences of the same instance of a reference, this is what is exported (a new reference is created):
Note:
- The BOM is not always kept.
- Some empty references, translated as type 308 entities, can be exported.
Important: Regarding the Product Graphical Properties: 
- When you start the export from an interactive session, the result is always WYSIWYG, no matter which menu item you may have selected.
- When you start the export from a non-interactive command (CAA command, batch monitor,...), the product graphical properties (in this case the visibility status) taken into account are those stored in the data base. In that case, to export graphical properties previously modified in an interactive session, do not forget to select Keep modifications before hitting the Propagate command.
 By default,
Export only shown entities is selected.
By default,
Export only shown entities is selected.
- when the visibility status is not the same for two different instances of a reference, the BOM is respected and kept.
- Curve and surface type
-
The default Standard option and the BSpline
option allow you to select which curve and surface types you want
to be generated.
If you leave the default Standard option selected the
curve and surface types created in the Part are kept as is.
If you select the BSpline option all curves and surfaces
are converted into B-splines.
 By default,
Standard is selected.
By default,
Standard is selected.
- Representation mode
-
If you select the default option Surface, solid decomposition will be identical in both the original model and the resulting file. Only the surfacic decomposition of the original model is stored.
Select Wireframe for the 3D visualization of solid edges to be identical in both the original model and the resulting file. Only the wireframe decomposition of the original model is stored. This may be useful in cases where curves are the only form of input accepted.
Select Solid-Shell to save Solids, Shells and Faces as IGES New Entities as follows:
V6 IGES Solid Manifold Solid B-Rep Object Entity (Type 186, Form 0) Solid (Closed) Shell Closed Shell Entity (Type 514, Form 1) Independent Shell Open Shell Entity (Type 514, Form 2) Face in a Shell Face Entity (Type 510, Form 1) Face Loop Loop Entity (Type 508, Form 1) List of Loop Edges Edge Entity (Type 504, Form 1) List of Start/End Loop Edges Vertices Vertex Entity (Type 502, Form 1) Plane Surface (support of Face) Plane Surface Entity (Type 190, Form 0) Note:
- For Loops, only the 3D Representation is exported
- All those new IGES entities have not been "tested" (IGES Norm 5.3) and the IGES/PDES Organization recommends that special consideration be given when implementing certain untested entities. Therefore if you do not know whether the receiver system will recognize those entities, we recommend that you do not use this option.
- The representation mode Solid-Shell requires IGES version 5.3 or higher.
 By default,
Surface is selected.
By default,
Surface is selected.
- Name of Author
-
Enter your name. This information will be transferred to the Global Section of the IGES file at export.
 By default,
Name of Author is empty.
By default,
Name of Author is empty.
- Author's Organization
-
Enter the name of your organization. This information will be transferred to the Global Section of the IGES file at export.
 By default,
Author's Organization is empty.
By default,
Author's Organization is empty.
- Export Units as
-
Let's you define the unit to be used for export. This unit can be different from the V6 file.
With Keep User Unit, the IGES file unit will be :
- the unit defined in tab, if the IGES Norm recognizes it,
- the Millimeter (mm) otherwise.
Important: Units like the ones named Feet, Inch, Decimal are not recognized by IGES Norm. If such Units are selected in tab and if the option selected is Keep User Unit, the IGES file unit will be the Millimeter (mm).
![]() By default,
Keep User Unit is selected.
By default,
Keep User Unit is selected.
