Before computing mean dimensions, apply the Edit
Parameters contextual command to the feature of interest to
display parameters, then take a look at the 3D shape you have just opened.
The 3D shape includes three tolerance parameters as shown below.
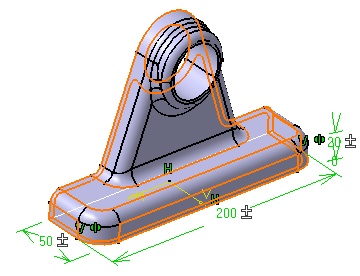
Click Mean Dimensions
 .
.
A dialog box appears informing you that the operation is performed. You
then just need to update the 3D shape to observe the result.
Click Update All
 to integrate the modifications to the 3D shape.
to integrate the modifications to the 3D shape.
Note that the update options set for your session (for more
see General) do not affect the Mean Dimensions command
behavior: you always have to explicitly update your 3D shape. Mean dimensions are displayed around the
3D shape.
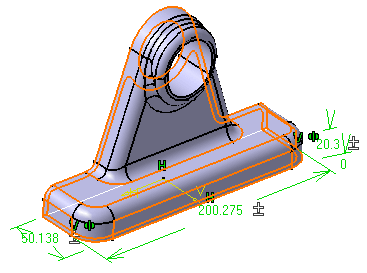
If you wish to go back to the previous state, click Mean Dimensions
 again.
again.
A dialog box appears informing you that the 3D
shape will be resized to
nominal dimensions.
Original tolerance values, when re-computed, are
always
expressed in numerical values.
Click OK to confirm.
An additional message appears to inform you that the operation is
performed and prompts you to update the 3D shape.
Click OK
to close the message window.
Click Update All
 to resize the 3D shape to nominal dimensions .
to resize the 3D shape to nominal dimensions .
Keep in mind the following:
- To ensure that you can run the command properly, do not use
features having the same name.
- If parameters are driven by formulas, the application
deactivates these formulas to compute mean dimensions.