Edit an Existing Environment
This task explains how edit an existing environment.
Select the Start > All Programs >
MyProduct > Tools >
Environment Editor
V6R2012
command.
You can also start the environment editor by running the
command: C:\Program Files\Dassault Systemes\B211\intel_a\code\bin\catiaenv
C:\Program Files\Dassault Systemes\B211\win_b64\code\bin\catiaenv The Environment Editor
appears. Note: the screenshots in this scenario
describe how to perform the scenario for the CATIA brand on Windows.
But the scenario works in the exactly the same way for all other brands.
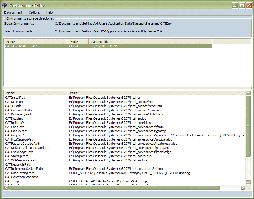
Note that the list of existing environments is displayed
in the Environment name list. The list will contain all the
environments detected in the current environment folder. The
first environment is selected by default.
When an environment in the list is selected, click the right
mouse to display a contextual menu of environment manipulation
commands.
The Mode field indicates one of two possible values:
- User: indicates that the environment was set up using
your userid, is visible to you and can only be accessed
by you (you cannot see anybody else's user environments)
- Global: indicates that the environment was set up by
somebody belonging to the Administrators group, or who has
the privileges assigned to the Administrators group (you
can see all the global environments on your computer): this
is what you will see after an initial installation on your
computer.
Only an administrator can modify global environments.
This means that you will only see in the Environment
name list the names of environments you created, or which
are common to all users. You can only edit environments
which belong to you. Furthermore, if you select a global
environment as end user, you will be able to display an
environment, but not edit it.
The Last Modified field specifies the date and time the environment
was last modified. The Environment storage directories area
displays the current storage location for both global and user
environments. This setting is the location you specified during
installation.
To reset environment storage directories, select the
Options > Set User Storage Directory or the Options
> Set Global Storage Directory command to display a file explorer,
then explore your filetree to select the directory, and click OK.
Any environments created from now on will be stored in these
locations. You can
use the storage directory settings to filter the list of environment
names and types displayed. For example, if you created both
global and user environments in the same user storage directory,
selecting the user storage directory will now only display the
user environments, and not the global environments.
To display the variables for any environment, click
the environment name.
For example, click the name of the default
global environment
set up at installation.
This will be the only environment name in the list after
a default installation. However, once you create new environments,
these will also be displayed in the list.
The variables and their values are displayed:
- the variable name is displayed on the left
- and the value (path) for the corresponding variable
is displayed to the right.
Click a variable name in the list.
The variable name and its corresponding value are highlighted:
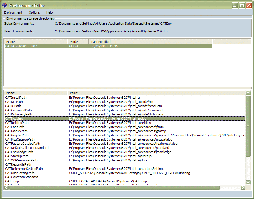
For example, the default path for the CATDocView variable
in our example is:
C:\Program Files\Dassault Systemes\B211\intel_a\doc
However, you may have installed the online documentation
in a different folder.
If you are authorized to edit the variable, click the
variable value to be able to edit it, then type in the new value.
For example, you would type in the new path for the variable
CATDocView. The value of the variable is reset in the Environment
Variables field.
Click OK.
CSIDL Values in Environment Variable Paths
There are a number of folders that are used frequently by applications,
but may not have the same name or location on any given system. For example,
the system folder is "C:\Windows" on Windows XP. CSIDL values provide a
unique system-independent way to identify these special folders.
Consequently, CSIDL values are now part of paths pointed to by environment
variables. The variables concerned are:
- CATUserSettingPath
- CATTemp
- CATReport
- CATErrorLog
What Is the DSKEY_TMPDIR Key?
The TMP and TEMP variables pointing to the current temporary file path
on your computer are not necessarily activated.
The DSKEY_TMPDIR key points to the current temporary file path on your
computer which is obtained as follows:
The software does not verify that the directory specified by the TMP
or TEMP environment variables exists. The temporary file path is obtained
as follows:
- the path specified by the TMP environment variable.
- the path specified by the TEMP environment variable, if TMP is not
defined.
- the Windows directory, if both TMP and TEMP are not defined.

Create an Environment using the New
Command
This task explains how to create a new environment using the Environment
Editor.
Select the Start > All Programs >
MyProduct > Tools >
Environment Editor
command.
Select the Environment > New command to display
the following dialog box:
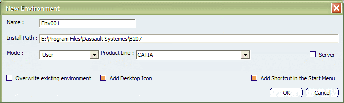
Enter the name of the environment to be created.
Enter the path of your installation folder.
The default installation folder path is: C:\Program Files\Dassault Systemes\B211\intel_a
C:\Program Files\Dassault Systemes\B211\win_b64
If you logged on as administrator, enter the environment
Mode.
The type can be user or global (global is available only
for administrators only). If you are logged on as a normal end
user, the type is set automatically to "user".
Check the Server option if the environment
is to be a server-type environment.
Check the Overwrite existing environment
option to overwrite an existing environment.
Click OK to create the environment.
The environment is created in: C:\Documents and Settings\User\Application Data\DassaultSystemes\CATEnv
where "user" is "All Users" for a global environment, or
"myuserid" for a user environment.

Copy an existing environment using
the New from... command
This task explains how to create a new environment using the Environment
Editor by copying an existing environment.
Select the Start > All Programs >
MyProduct > Tools >
Environment Editor
command.
Select an environment and click Yes to confirm you want
to modify it.
Select the Environment > New from... command
to display the following dialog box:
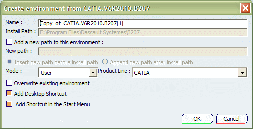
Customize the name of the environment to be created.
Enter the path of your installation folder.
The default installation folder path is: C:\Program Files\Dassault Systemes\B211\intel_a
C:\Program Files\Dassault Systemes\B211\win_b64
Check Add a new path to this environment
and specify where to insert the path (before or after the install path)
using the appropriate options if required.
If you logged on as administrator, enter the environment
mode.
The type can be user or global (global is available only
for administrators only). If you are logged on as a normal end
user, the type is set automatically to "user".
Check the Overwrite existing environment
option to overwrite an existing environment.
Click OK to create the environment.
The environment is created in: C:\Documents and Settings\User\Application Data\DassaultSystemes\CATEnv
where "user" is "All Users" for a global environment, or
"myuserid" for a user environment.
Setting Correct Authorizations for End Users on Windows
Server environments use by default the folder referenced
by the CSIDL_COMMON_APPDATA path for the CATUserSettingPath
variable. This folder is usually:
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data
and is used to contain a variety of files, including user
settings located in the Dassault Systemes folder. Typically,
the authorizations given to the CATUserSettingPath may not be
sufficient. By default, the folder:
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data
does not provide write access for normal end users. The default
authorizations on the folder:
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users
and all the subfolders it contains are:
Administrators - Full Control
Power Users - Change (Read/Write)
Everyone - Read
System - Full Control
Consequently, make sure that end users using server-type
environments have sufficient authorizations (MODIFY+WRITE) for
at least the folder:
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Dassault Systemes
to be able to write their settings to (and modify their settings
in) this folder.

Create and Delete User-Defined Variables,
and Edit Variables using the Contextual Menu
This task explains how to create and delete user-defined variables, and
edit any variable, using the contextual menu.
Select the Start > All Programs > MyProduct > Tools
>
Environment Editor
command.
To display the variables for any environment, click
the environment name and confirm that you want to modify it.
Without selecting a variable, right-click on the variable
list to see the contextual commands:
New Variable Delete Variable Edit Variable
To create a user-defined variable, select the New Variable command to display the Variable Editor dialog box:
and enter the variable name, its value, and a comment if
required, then click OK.
To delete a user-defined variable, select the variable,
then select the Delete Variable command, then click Yes
to delete the variable.
Note that you can delete only user-defined variables created
using the New Variable command, and not official
variables.
To edit any variable, select the variable, select the
Edit Variable command to display the Variable Editor dialog
box:
then enter its new value and click OK. Note that the variable
name and comment field are not available if you are modifying
an official variable. However, the name, value and comment are
editable if you are editing a user-defined variable only.
Do not forget to save your changes by selecting the
Save command, also in the contextual menu.
|
![]()





