Create an Adaptive Swept Surface
You can create adaptive swept surface.
Click Adaptive Sweep
 in the Sweeps sub-toolbar. in the Sweeps sub-toolbar.
The Adaptive Sweep Definition dialog box appears.
Select the Guiding Curve.
If no guiding curve already exists, use the contextual menu in
the Guiding curve box to create, either a line, or a
boundary.
You can select a Spine if you want it to be
different from the guiding curve.
Selecting a Reference Surface is optional. It
is the surface on which the guiding curve lies and is used to define the
axis system in which the swept surface is created. Indeed one of the axes
(H or V) is defined as tangent to the reference surface.
In our example, may you wish
to define a reference surface, select the xy plane. Otherwise the
mean plane is used as default.
If you choose a boundary as the guiding curve, the
reference surface automatically is the surface to which the boundary
belongs.
You can de-select a reference surface using the Clear Selection
contextual menu on the Reference surface box.
Select the Sketch to be swept along the
guiding curve .
An axis-system is displayed defining the plane in
which the first section is created.
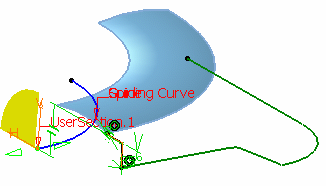
Select the end point of the guiding curve to create
another section.
The axis-system is displayed at this new section.
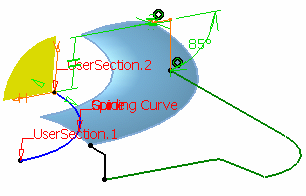
Click Sweep sections preview to have a quick
wireframe preview of the adaptive sweep surface.
This option lets you see the evolution of the sketch along the
guide curve.
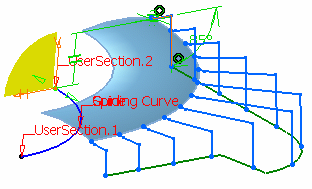
Three contextual menu items are available on the
manipulators:
-
Create
a section here: lets you create a section at the
manipulator's place. A new point is dropped on the guide curve with
the corresponding ratio. If the guide curve is closed, the created
point is a 3D coordinates point.
-
Use
interpolated manipulator: the interpolation value between the
section parameters is computed. You can move the manipulator along
the guide curve to visualize the parameters evolution.
-
Show all sections' constraints:
lets you visualize all the sections and their constraints at the
same time.
The list in the Sections tab is automatically updated
with:
- the first section being at the intersection of the selected
sketch and guiding curve
- the second section at the selected point on the guiding curve.
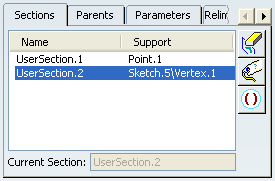
- Click
 or choose the
Remove Section contextual menu, to delete a section from
the swept surface. The first section cannot be deleted. or choose the
Remove Section contextual menu, to delete a section from
the swept surface. The first section cannot be deleted.
- Click
 or choose the Rename Section contextual
menu, to give a new - more explicit - name to any user section.
or choose the Rename Section contextual
menu, to give a new - more explicit - name to any user section.
- Click
or choose the Activate Section / Deactivate Section
contextual menu, to respectively activate or deactivate
adaptive sweep sections.
Set the Deviation
value: it corresponds to a point tolerance.
Decreasing this value increases the precision but leads to slower
performance.
By default the value is 0.1mm.
Select the Angular correction check box
to smooth the sweeping motion along the reference surface. This may be
necessary when small discontinuities are detected with regards to the
spine tangency or the reference surface's normal. The smoothing is done
for any discontinuity which angular deviation is smaller than 0.5 degree,
and therefore helps generating better quality for the resulting swept
surface.
By default, the angular correction is set to 0.5 degree. Click Preview.
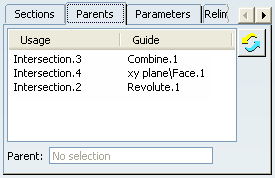
Click the Parents tab to display the elements
making up the sweep.
Click the Parameters tab to display and
redefine the constraints on a given section.
Use the combo list to define the current section.
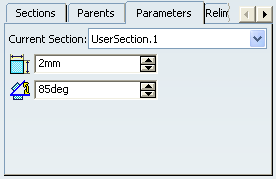
Change the constraint value to 5mm, and click
Preview.
The modified sweep is previewed:
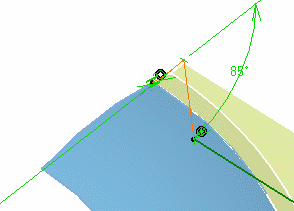
Click OK to create the swept surface.
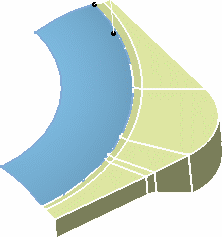
The surface (identified as Adaptive sweep.xxx) is added to the
specification tree.

Create or Select a Sketch
Once you have selected the guiding curve, you
can select an existing sketch or create one by clicking either
 or selecting the Create
Sketch contextual item on the Sketch box to start the
sketcher within the adaptive sweep context. or selecting the Create
Sketch contextual item on the Sketch box to start the
sketcher within the adaptive sweep context.
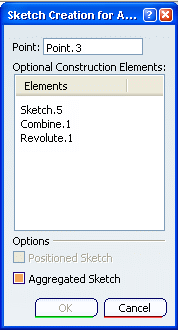
In this case, the Sketch Creation for Adaptive Sweep dialog box is
displayed, and allows you to define the construction elements for a new
sketch in relation to existing geometry.
Select a point, used to
position the sketch on the guiding curve, as well as the origin of the
sketch. If needed, select
construction elements (another guiding curve, support surfaces, and so
forth).
The selection in the geometry implies a global selection of the
3D elements. Two options are available:
- Positioned Sketch: this option lets you position the
created sketch according to the swept surface inputs. Therefore, if
you modify the swept surface, the sketch is automatically updated.
- Aggregated Sketch: this option lets you aggregate
the sketch under the swept surface feature in the specification
tree.
Click OK.
The system automatically loads the Sketcher
workbench, and provided the correct option is active, sets the sketch
plane parallel to the screen. You can then define a new sketch.
Once you exit Sketcher by clicking
 ,
you return to the Adaptive Sweep command after the sketch selection,
as described above in step 5. ,
you return to the Adaptive Sweep command after the sketch selection,
as described above in step 5. This local definition of the sketch is particularly
interesting as it allows to redefine the swept surface simply by
editing the local sketch (add/remove construction elements, or
constraints for instance).
Note:
If you are a DS Passport customer, you can read the QA00000007443 article from the Knowledge Base for more information about sketch selection.

Relimit the Swept
Surface
The Relimitation tab enables you to create
a multi-sections swept surface using a closed guide. It lets you specify
the relimitation type.
|
![]()
 or selecting the Create
Sketch contextual item on the Sketch box to start the
sketcher within the adaptive sweep context.
or selecting the Create
Sketch contextual item on the Sketch box to start the
sketcher within the adaptive sweep context.
![]()





 or choose the
or choose the
 or choose the
or choose the 





