Select . The Create Import dialog
box appears.
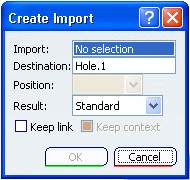
In the Import box, select the object from
which you want the external and internal references to be created.
Note:
The supported elements are:
-
wireframe and surface features
-
volumes
-
sketches
-
bodies
-
parameters (if they are set as visible in )
-
sub-elements (face, edge, vertex)
-
solid functional sets (SFS)
-
functional specifications
- functional sets.
The last three elements are only available with the Functional Modeling Part workbench.
The name of the object appears in the Import
box.
In the Destination box, select the destination to aggregate the import to be created. By default, the destination is the in work
object.
In the Position list, select the position of the import to be created relative to the destination:
-
After: the element is positioned after the reference.
-
Before: the element is positioned before the reference.
- Inside: the element is positioned inside the reference.
The element will be imported in the place you selected. Note:
- The list only presents choices that are possible.
- The default value is After (when the choice is possible).
In the Result list, select the kind
of result you want to have after the duplication.
Note:
Indeed, some features have more than one geometrical result. For
instance, a sheetmetal body can have a form result and a flat
result.
Select the type of associativity:
Click OK when
satisfied.
- The created imports are inserted
in the specification tree.
- The solid external references are created in a solid body or a body according to
the option Enable
hybrid Design defined in tab.
|