1D Property Section Types | |||||
|
| ||||
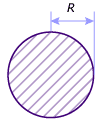
Rod
You can choose this option for any section that works in traction/strain. You then need to specify the section area in the Section area box.
![]()
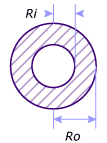
Thin Box Beam
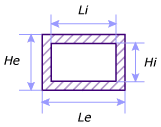
- Li is the inner width.
- Hi is the inner height.
- Le is the outer width.
- He is outer height.
![]()
Thin I Beam
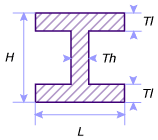
- L is the width.
- H is the height.
- Tl is the thickness associated to the width.
- Th is the thickness associated to the height.
![]()
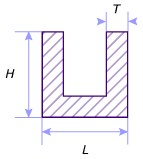
Thin T Beam
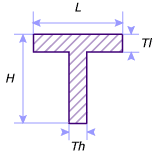
- L is the width.
- H is the height.
- Tl is the thickness associated to the width.
- Th is the thickness associated to the height.
![]()
Thin X Beam
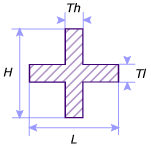
- L is the width.
- H is the height.
- Tl is the thickness associated to the width.
- Th is the thickness associated to the height.
![]()
User-defined Beam
This option works for any type of section. You have to specify the following characteristics:
- S is the section area.
- Ix, Iy, Iz are the three components of the inertia matrix of the beam expressed in the principal axis of the beam (axis in which the matrix is diagonal).
- Ix is the torsion coefficient.
- Iy is the area moment of inertia in the XZ-plane.
- Iz is the area moment of inertia in the XY-plane.
- Shear center Y is the Y-coordinate of the shear center in the section axis, centered at the center of gravity of the section.
- Shear center Z is the Z-coordinate of the shear center in the section axis, centered at the center of gravity of the section.
- Shear ratio XY is the ratio between the cross-sectional area (A) and the shear area (Ay),
area section that works in shearing in the XY-plane (case of a
short beam). This ratio should be greater than one.
Shear ratio XY = A / Ay
- Shear ratio XZ is the ratio between the cross-sectional
area (A) and the shear area (Az), area section that works in
shearing in the XZ-plane (case of a short beam). This ratio should be greater than one.
Shear ratio XZ = A / Az
| Important: The availability of this option depends on your available licenses. See Licensing. |
![]()
Beam from Surface
This option works for any type of section. You have to select a surface.
| Important: The availability of this option depends on your available licenses. See Licensing. |