More about Pasting Objects as Special | ||
| ||
Paste Formats
The list of available paste formats depends on the object type.
- As specified in Part document: the object is copied as it has been created but generally without its design specifications. For instance, surface features cannot be copied with their design specifications whereas pads can.
- As Result With Link: the object is copied without its design specifications and is linked to the original object. In other words, whenever the original object is modified, the copied object may be manually updated to reflect the changes.
- As Result: the object is copied without its design specifications and without any link with the original object. It is considered as an autonomous entity. When using this option, solids and curves are created. However, note that regarding ordered geometrical sets, hybrid bodies and part bodies, only the final result is copied.
- As specified in Product Structure: the source instance is duplicated and the link to the source reference is kept. A new instance of the source is created with the same reference as the source. For detailed information, see VPM Physical Editor User's Guide: Paste Special.
- As specified in Assembly
- As Result With Link Flat Mode to paste a flattened object.
- As Result all views: the sheetmetal object is copied as a solid with both folded and unfolded views. For more information, see SheetMetal Design User's Guide.
- As Result With Link all views: the sheetmetal object is copied as a solid with both folded and unfolded views and with a link to the original object. This means that whenever the original object is modified, the solid is updated accordingly. For more information, see Generative Sheetmetal Design User's Guide.
The following table sums up which feature can be pasted "as special" using which format:
| Part body | Body.n | Pad | Sketch | Geom. set | Surface feature | Parameter | Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As specified in Part document | ||||||||
| As Result With Link | ||||||||
| As Result | ||||||||
| As specified in Assembly | ||||||||
| As specified in Product Structure | ||||||||
| As Result With Link Flat Mode | ||||||||
| As Result all views | ||||||||
| As Result With Link all views |
![]()
General Rules for Managing the Paste Destination
The paste destination you select has an impact on the way the object is pasted. In addition to this, specific rules are applied when pasting geometrical features and power copies.
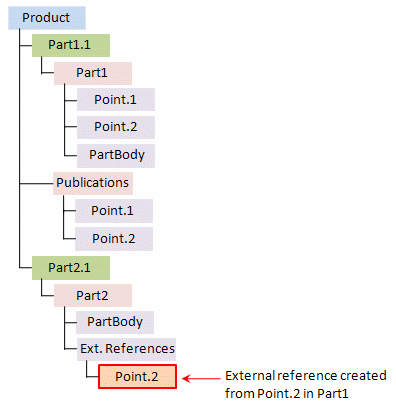
- If the paste destination you select is not appropriate, an error window is displayed. For instance, pasting directly in an "External References" node is forbidden.
- If the paste destination is a geometrical feature, the element is pasted after the selected geometrical feature (if applicable).
- If the paste destination is a body (e.g. part body, geometrical set), the application pastes the element in the body and in last position.
- If the paste destination is a part:
- For a geometrical feature, the application tries to find a destination based on the current feature.
- For a body or a set, the element is pasted under the part.
- If no paste destination has been selected or if you are working with power copies, the application tries to paste the element in or after the current feature.
The rules that apply when creating geometrical features also apply when pasting them as shown in the following table:
| Can be pasted in... | Part body (created before V5R14) | Part body (created from V5R14) | Geometrical set | Ordered geometrical set |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geometrical set feature | ||||
| Part body | No | No | No | No |
| Geometrical set | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Ordered geometrical set | No | Yes | No | Yes |
As far as power copies are concerned, the rules that are applied are the following if the feature to be pasted is a geometrical set or an ordered geometrical set:
- If the geometrical set was located under the part as defined in the power copy, the feature is pasted under the part.
- If the geometrical set was a sub-geometrical set (i.e. located under a body or under another set), the feature is pasted according to the current feature.
![]()
Pasting Solid Objects Using the Specification Tree
Solids pasted As Result With Link are identified by a specific symbol in the specification tree.
As Result With Link
- When opening a document containing a body pasted As Result
With Link, the corresponding symbol displayed in the
specification tree is
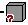 . This
symbol means that the pointed document has been found but not loaded.
To correct this, right-click the object in the tree then select Load, or select
then click Open
pointed component. The symbol will then change to
. This
symbol means that the pointed document has been found but not loaded.
To correct this, right-click the object in the tree then select Load, or select
then click Open
pointed component. The symbol will then change to
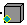 to
indicate that the object has been copied from a document different from
the document it has been pasted to and that it is synchronized with its
reference.
After this synchronization step, the document containing the body
pasted As Result With Link needs to be updated to
integrate the changes from the pasted body. This update requires
to open the document first and then, to update it.
If the updated document contains also a body pasted As
Result With Link in another document, the same mechanism
applies to the latter, i.e. synchronization step then, a second
update of the document.
to
indicate that the object has been copied from a document different from
the document it has been pasted to and that it is synchronized with its
reference.
After this synchronization step, the document containing the body
pasted As Result With Link needs to be updated to
integrate the changes from the pasted body. This update requires
to open the document first and then, to update it.
If the updated document contains also a body pasted As
Result With Link in another document, the same mechanism
applies to the latter, i.e. synchronization step then, a second
update of the document.Important: - The symbol is also displayed if the pointed object is deleted.
- This behavior also applies to surfaces, not only to solids.
- If you deactivate a solid pasted As Result With Link,
its symbol in the specification tree changes from
 to
to
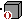 to indicate that the external
link is deactivated (the solid is isolated just like a datum) but not
the geometry.
to indicate that the external
link is deactivated (the solid is isolated just like a datum) but not
the geometry. - When a feature is pasted As Result With Link, the color (if any) is kept. However, note that this color is not considered as a synchronizable information: the color is only copied when the feature is pasted and therefore, you will not be able to update it if the color of the original feature is modified.
![]()
Pasting Surface Objects Using the Specification Tree
The type of the surface object to be pasted as well as the paste location you select have an impact on the paste result when pasting As specified or As Result/As Result With Link.
As specified in Part document
- Elements aggregated by a geometrical feature cannot be pasted As specified. In the example below:
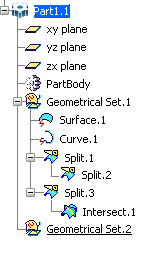
If you copy "Split.2" then paste it onto "Geometrical Set.2", the Paste Special dialog box only displays As Result and As Result With Link. The reason is that "Split.2" is not an autonomous element and belongs to "Split.1". However, if you copy "Split.1" with "Split.2", you can paste both elements As specified because "Split.1" and "Split.2" are considered as a single entity:
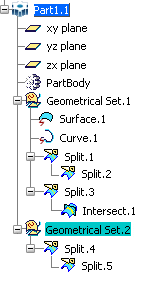
If you copy then paste "Split.1" As Result (or As Result With Link), only "Split.1" is pasted.
- If you copy an internal import As specified, you will generate an import (internal or external according to the target document) of the original import's reference.
As Result/As Result With Link
- is an explicit action. As a consequence, a feature pasted As Result With Link can be pasted as an external reference but will always appear in Show mode, even if theCreate external references in Show mode check box is not selected in .
- When a feature is pasted As Result with Link, the color (if any) is kept. However, this color is not considered as a synchronizable information: the color is only copied when the feature is pasted and therefore, you will not be able to update it if the color of the original feature is modified.
- If a surface or wireframe feature has been renamed via prior to copying, this feature is pasted as "Result of SurfaceUserName" when using As Result or As Result With Link, and as "Copy of SurfaceUserName" when using As specified in Part document only when the In the main object check box is selected in . This "Copy of ..." or "Result of ..." prefix is used only if the document in which the element is pasted already contains a feature renamed "SurfaceUserName". If the name "Copy of SurfaceUserName" conflicts with the name of an existing feature, the system will try to name the pasted feature "Copy (2) of SurfaceUserName" and if this new name is already used, it will try "Copy (3) of SurfaceUserName" and so on. If you paste in an empty CATPart, the name "SurfaceUserName" does not conflict with any other name and thus, can be kept as is. When the No name check or Under the same tree node check box is selected, no prefix is added.
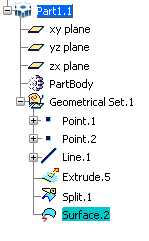
- If you copy then paste As
Result a surface element which is not a point, a line, a surface or
a plane, the result will be a line, a curve, a circle or a surface
according to the geometrical dimension and the type of the element. In the example below, when "Split.1" is copied then pasted
As Result onto "Part1", the resulting element is a surface ("Surface.2"
in the example below):
- If the dimension cannot be determined (this is the case for features
containing several geometrical domains with a different dimension such as
a point and a line or a line and a plane), the result is a 3D datum. In
the example below, when "Intersect.1" (which contains a point and a line)
is copied then pasted As Result (or
As Result With Link) onto "Part1", the
resulting element is a 3D datum representing a surface, a curve and a
point:

- If you copy then paste As Result With Link a surface element which is not a point, a line, a surface or a plane, then the result is a curve or a surface according to the geometrical dimension. The result can be neither a line, nor a circle because it is not possible to synchronize a line or a circle with a general curve.
- Pasting a geometrical set As Result is recursive, i.e. all the
elements located below the geometrical set are also be pasted. In the example
below, when copying "Geometrical Set.1" As Result ...
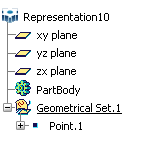
... then pasting it onto "Part1", the resulting copy (named "Geometrical Set.1") contains all the elements included in "Geometrical Set.1" and "Point.1" has been incremented to "Point.2":
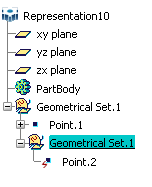
If the In the main object check box is selected in , the "Result of" prefix is added to the copy. In our example, it would be "Result of Geometrical Set.1".
![]()
Pasting Sub-elements
Specific rules are applied when using the Copy command on sub-elements before pasting them.
- If you select a sub-element such as a face, an edge or a vertex in the geometry then copy it, the copy will include the first element that can be copied and not only the sub-element itself. For instance, if you copy a face of a pad, the whole pad will be included in the copy.
- You cannot copy a publication of a sub-element (edge, face or vertex). If you try to do so, an error message will appear.