Simulation Logic Creation and Aggregation Rules | ||
| ||
Glossary
Some terms frequently used in this user's guide needs to be defined in context of the System and Device Designer workbench.
Resources represent devices (such as a tool, robot, or machine) used to build a manufactured product. Please refer to the Resource Definition and Layout user's guide for a detailed description of the different resource types.
Simulation logics emulate the behavior of a resource.
Leaf resources are non-organizational resources. In the System and Device Designer context, a simulation logic is usually associated to a leaf resource.
Systems are organizational resources. In the System and Device Designer context, this organizational resource usually aggregates simulation logics of devices (or leaf resources).
![]()
Simulation Logic Creation Rules
For all resources, the simulation logic can be created in the reference of the resource. For some resources (identified as programmable resources), the simulation logic can also be created in context of the first organizational logic containing the resource.
See a typical resource tree below.
The yellow star means that a simulation logic is associated to the resource.
- The programmable resources are: Robot, Worker, Inspect, NC Machine, Control Device, Storage, Transport and User Defined.
- The non-programmable resources are: Industrial Machines, Tool Devices, Sensors, LogicControllers and Conveyors.
For a programmable device like a robot, the simulation logic emulates the program loaded in the device controller. So, the simulation logic of the device is created in context of the organizational resource gathering the physical representation of the device and its controller. In fact, the rules to create the simulation logics are similar to the rules to create motion controllers. As a simulation logic can only trigger the tasks available in the same context, you have to create the simulation logic in the same context as the motion controller containing the tasks to run.
![]()
Simulation Logic Aggregation Rules
Simulation logics on resource can be aggregated. However, a number of rules applies which mainly concern the role of Organizational and Area resources in the resource structure.
- Simulation logics can only be aggregated in the simulation logic of an organizational resource.
- In the simulation logic of an organizational resource, the user can only map the simulation logics of sub-resources. The functions allowing to interact with the 3D representation or the mechanism of the resource are not allowed.
- The simulation logic of an organizational resource can only aggregate the first level sub-resource logics. The logics below the first resource are ignored. This rule is applied whatever the sub-resource types: organizational or non-organizational. There is an exception the Area resource. As this resource type cannot support a simulation logic, this resource is transparent. The organizational resource logic aggregates the first logic resources found below an Area resource.
Example 1:
RobotA.1 aggregates the logic of H1L_R.1 and RobotA.2 aggregates the logic of H1L_R.1.
 |
 |
Station aggregates the logic of RobotA.1, RobotA.2 (the first resources below Station), GENERIC_JIG_8.1, GENERIC_JIG_6.1, GENERIC_JIG_4.1, GENERIC_JIG_3.1 (the first resources below Station as we ignore the Area resource). 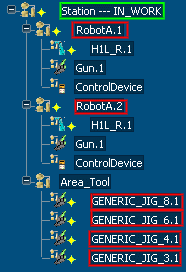
Example 2:
From the previous example, we have removed the RobotA.1 logic. In this case, Station cannot aggregate the H1L_R.1 logic because only the first level sub-resource logics can be aggregated even if no simulation logic is associated to the resource.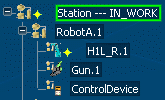
So, it is mandatory to associate a simulation logic to RobotA.1 to run the H1L_R.1 logic via the aggregation to the RobotA.1 level.
Example 3:
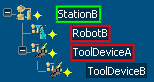
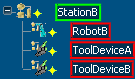
StationB aggregates the RobotB and ToolDeviceA logics. It is impossible for StationB to aggregate the ToolDeviceB logic.
- ToolDeviceA cannot aggregate the ToolDeviceB logic because only organizational logic can aggregate sub-resource logics.
- Station B cannot aggregate the ToolDeviceB logic because only the first level sub-resource logic can be aggregated.
A correct structure can be: